
Here's The List Of 2025’s Best Mesh WiFi Systems for Connected Living
A mesh WiFi system forms the backbone of your connected home, ensuring your devices stay responsive, synchronized, and online 24/7.
The latest news on the biggest technology and communications companies.











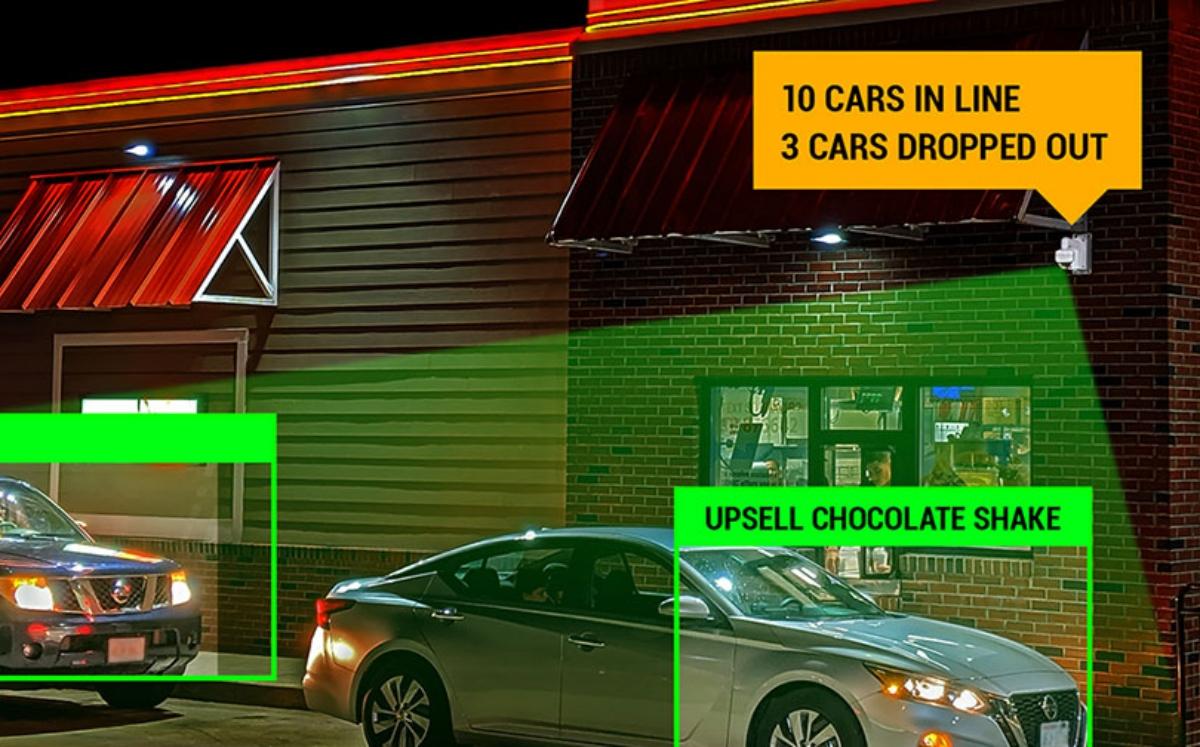















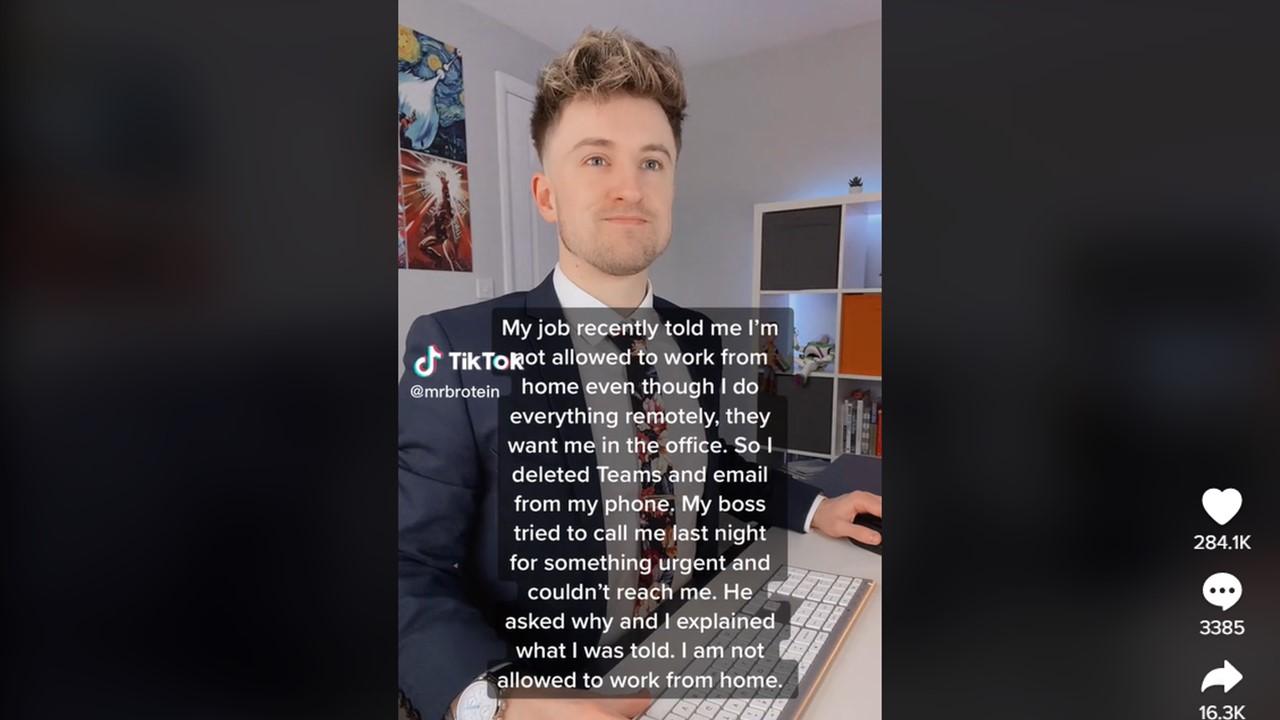



















© Copyright 2026 Market Realist. Market Realist is a registered trademark. All Rights Reserved. People may receive compensation for some links to products and services on this website. Offers may be subject to change without notice.