
Saul Perez
Disclosure: I am in full compliance with all ethics and other policies for Market Realist research analysts. I am not invested in securities that I cover on Market Realist.
More From Saul Perez
Financials Why Wells Fargo leads in loans
The bank has always focused on its bread and butter revenue-earning stream: loans. Over the years, Wells Fargo slowly realized its goal of achieving a strong market share in lending.Financials Must-know: Determining a bank’s value
The first challenge is that banks are highly regulated and any change in regulations has a huge impact on the valuation of a bank—the second challenge is that it’s difficult to determine cash flow for a bank because both debt and reinvestment are difficult to calculate.Financials Why Wells Fargo has the highest net interest margin
Maintaining a high net interest margin has always been part of Wells Fargo’s (WFC) strategy. Wells Fargo has consistently been better than the industry’s average net interest margin.Financials Must-know: Putting the price–to-book value ratio in perspective
We explored the most commonly used valuation metric for financial companies—the price-book value. We also understood the relation between price-book value and return on equity.Financials Must-know: Is Wells Fargo making boring attractive for investors?
Wells Fargo’s (WFC) broad operation level strategy over the long run can be described by two words—slow and steady. It doesn’t take many risks. It’s stable and boring.
Traditional assets: Defining active and passive management
Active asset management refers to those asset managers that essentially try to outperform the average market return, a benchmark, or a hurdle rate that may have been set internally.Financials Why low funding cost is an advantage for Wells Fargo
If a bank is able to keep its cost of deposits low, it will have a competitive advantage. Wells Fargo has the lowest cost of deposits among its peers—despite having a very high deposit base.Financials Why Wells Fargo focuses on non-interest income
Wells Fargo wants to maintain a balance between its interest income from loans and non-interest income. Non-interest income accounts for nearly 49% of Wells Fargo’s revenues.Financials Why cross-selling is part of Wells Fargo’s strategy
Wells Fargo’s (WFC) first, and possibly the most important, operational strategy is focusing on cross-selling. It’s the most important pillar of its operational strategy.Financials Why Wells Fargo uses human resources as a strategic tool
Wells Fargo (WFC) believes that people are a competitive advantage source. Integrating sound human resource practices lies at the core of Wells Fargo’s strategy.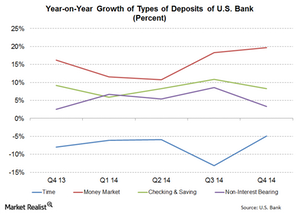
Low-cost deposit growth is a key strength for U.S. Bank
U.S. Bank does well in increasing its low-cost deposit base. In 4Q14, money market deposits grew the fastest at 19.7%—compared to 4Q13.
The main players in asset management
The efficient market hypothesis maintains that the market prices everything correctly and so it isn’t possible to outperform the market in the long run.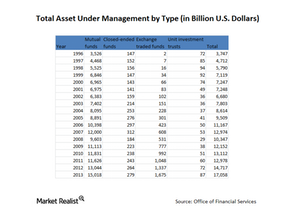
How big is the asset management industry?
Audited and verified annual figures at the end of 2013 indicate that total assets under management of US registered investment companies equalled nearly $17.1 trillion.
The salient features of mutual funds
There are investors who are willing to take on higher risk to generate above-average market returns. For these investors, active funds offer the optimal investment avenue.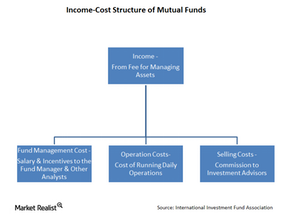
Show it: How mutual funds make money
In return for investing a client’s money, mutual funds charge a fee, generally an annual fee set as a percentage of the client’s assets. This fee is the only source of income for a mutual fund-focused asset manager.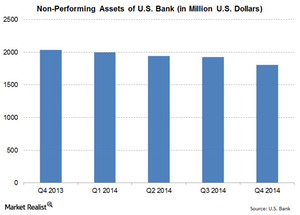
U.S. Bank’s non-performing assets declined in 4Q14
U.S. Bank’s (USB) non-performing assets were $1,808 million at the end of 4Q14. The ratio declined by 11.24%—compared to 4Q13.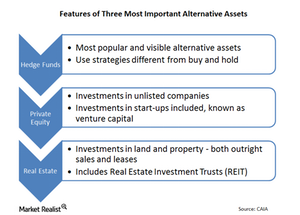
Private equity, hedge funds, and other alternative assets
Private equity is capital invested in companies that aren’t listed on stock exchanges. These alternative assets include venture capital.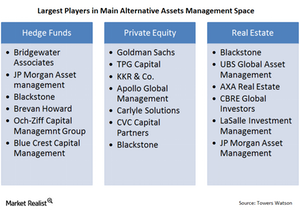
The many players in alternative asset management
Some players are present across the spectrum of alternative assets, but most alternative asset managers are present only in a particular asset area.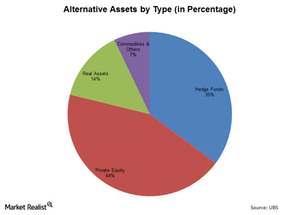
The relative share of the alternative asset management space
Alternative assets account for about 10% of the total global asset management industry that’s valued at $63.9 trillion. Private equity contributes most.
A brief overview of U.S. Bank
We’ll provide an overview of U.S. Bank. It’s the fifth largest retail bank in the US—by deposits and assets. At the end of September 2014, it held $391 billion in assets.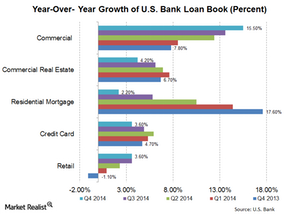
Why U.S. Bank’s loan growth showed interesting trends
You need to understand loan categories better in order to see some very interesting trends in U.S. Bank’s loan growth. Its loans are divided into five main categories.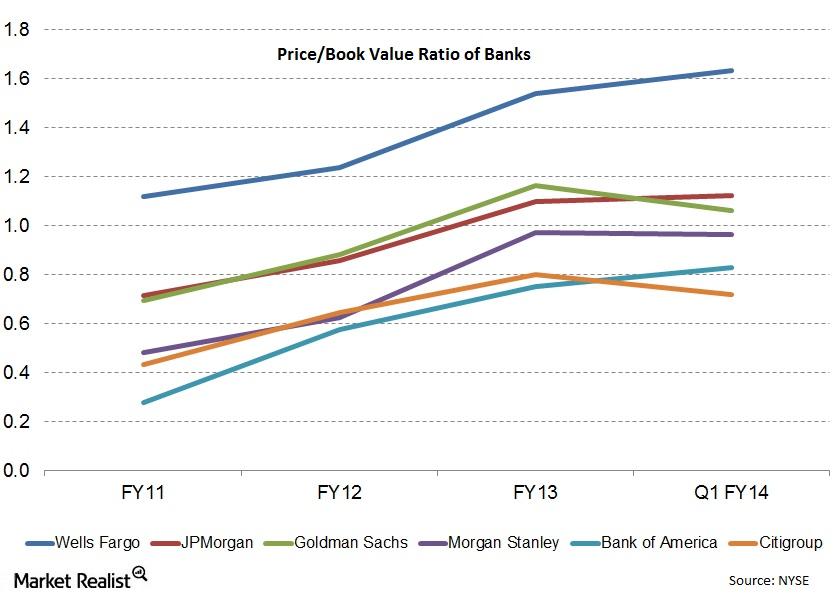
Why the price-to-book value ratio’s the most used valuation
The price-book value ratio is the ratio of the market value of equity to the book value of equity. Price stands for the current market price of a stock. Book value is the total assets minus liabilities, or net worth, which is the accounting measure of shareholders’ equity in the balance sheet.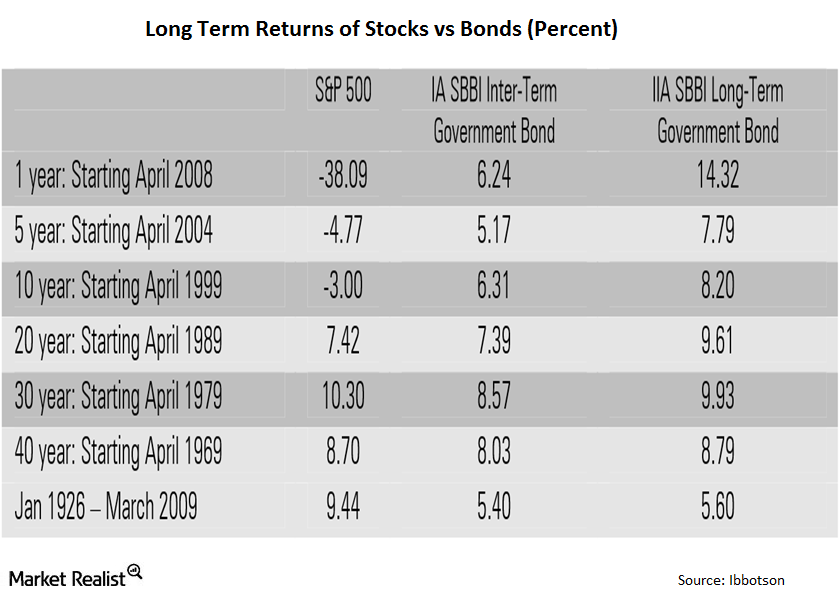
Stocks Beat Bonds over the Long Run By a Big Margin
The majority of investors believe bonds are safer than stocks. The main reason is that bonds pay regular interest.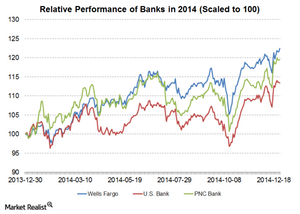
Valuation of PNC Bank is close to historical mean
PNC stock was trading at a PBV ratio of 0.75 in November 2012. Since then, the stock has seen a smart move up and trades at a PBV multiple of ~1.08.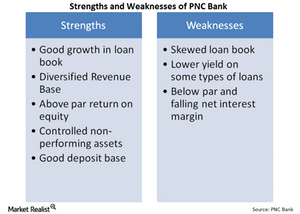
PNC Bank’s financial strengths outweigh its weaknesses
PNC Bank has done a good job at reducing its non-interest expenses, but the bank’s efficiency ratio still remains above 60%.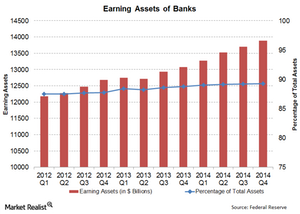
Why earning assets are an important indicator for the banking sector
The banking sector has shown a trend of increasing earning assets, because banks have focussed on becoming leaner and improving operational efficiency.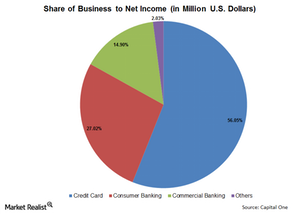
Analyzing Capital One’s business segments
Capital One (COF) can be understood best by breaking it into different business segments—Credit Card, Consumer Banking, and Commercial Banking.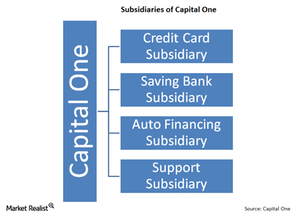
What are Capital One’s three main subsidiaries?
Capital One is organized into subsidiaries. Capital One’s principal subsidiary is a limited purpose credit card bank. It’s chartered in Virginia.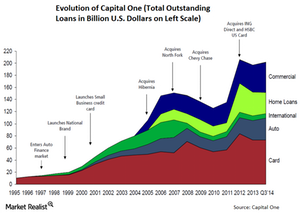
Capital One’s history: From credit cards to a diversified bank
Capital One’s history is shorter than other banks. In 1994, Signet Financial Corp. spun off its credit card business into a separate subsidiary—Capital One.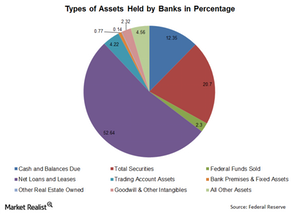
Why the composition of banking assets matters
The two main types of banking assets are loans and securities held.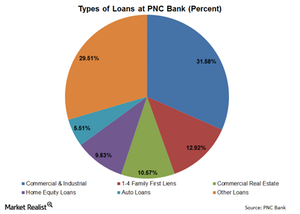
PNC Bank loan book carries some risks
PNC Bank’s loan book is skewed toward a few types of loans: commercial and industrial loans and 1–4 Family First Liens, about 44.5% of its total loans.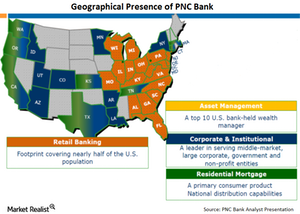
Does PNC Bank remain a strong long-term play?
With a strong presence in the East, South, and Midwest, PNC Bank offers community banking, wholesale banking, corporate banking, and asset management.Financials Must-know: Wells Fargo is strongly capitalized for future growth
A bank’s growth can be limited if it doesn’t have enough regulatory capital. If the bank doesn’t have enough capital, it will be forced to dilute its equity to raise capital.Financials Why Wells Fargo’s strategy is different from other banks
“Strategy” can be defined in many ways. Generally, strategy is a long-term plan. There are two main aspects to strategy—operational level strategy and human resource level strategy.Financials Why commercial lending is important to Wells Fargo strategy
The bank’s strategy is to not focus on any particular segment of industry. This helps it mitigate risk because the bank’s earnings and delinquencies are not dependent on any particular sector.Financials Must-know: Basel III’s shortcomings
Basel III addresses most of Basel II and II.5’s deficiencies. But it still has some shortcomings. Firstly, the increased regulatory capital required under Basel III will increase barriers to enter into the sector.Financials Why Basel II.5 corrected Basel II to improve banking regulations
Basel II.5 was essentially a revision of Basel II norms, as the existing norms often failed to correctly address the market risks that banks took on their trading books. Basel II.5’s main aim was to strengthen the capital base, and so the banks’ ability to withstand risk, by increasing banks’ capital requirements.Financials Why Basel II wasn’t good enough for reducing bank risks
Basel II was a comprehensive regulation that covered major sources of risks for banks. But it had a few major drawbacks. Firstly, it provided incentive to a bank’s management to underestimate credit risk.Financials Must-know: Why capital ratio is an important bank ratio
Capital ratio is also known as capital adequacy ratio or capital-to-risk-weighted assets ratio. Capital ratio is nothing but the ratio of capital a bank has divided by its risk-weighted assets. The capital includes both tier one and tier two capital.Financials Must-know: Why Basel I wasn’t a good fit for all banks
Although Basel I brought a worldwide standard in regulations, introduced the risk-weighted assets concept, and segregated capital, it had a few deficiencies.Financials Must-know: Understanding risk-weighted assets in banks
The second most important technical parameter used in banking regulations is risk-weighted assets (or RWA). If you’ve seen bank financial statements, then you might have noticed the “RWA” term there.Financials Must-know: Why capital in banking is important
Capital is important because it’s that part of an asset which can be used to repay its depositors, customers, and other claimants in case the bank doesn’t have enough liquidity due to losses it suffered in its operations.Financials Must-know: The different types of banking capital
The most important types of banking capital are common stock (or shareholders’ equity), preferred stock (or preferred equity), revaluation reserve, general provision, and hybrid instrument.Financials Overview: The basics of banking regulations
Banking regulations aim to ensure that the risks are minimized. If any unforeseen event occurs, then the interests of bank customers are protected. On a wider scale, the regulations also seek to absorb and minimize shock in the economy.Financials Must-know: The consequences of imprudent risk-taking by banks
We stated earlier that most banks are highly leveraged financial risk-takers. When things go awry, the results can be catastrophic, leading to huge losses or even to a bank closure.Financials Must-know: A thorough look at defining banking risk
Banking risk can be defined as exposure to the uncertainty of outcome. It’s applicable to full-service banks like JPMorgan (JPM), traditional banks like Wells Fargo (WFC), investment banks like Goldman Sachs (GS) and Morgan Stanley (MS), or any other financials included in an ETF like the Financial Select Sector SPDR Fund (XLF).Financials Overview: What you need to know about banking risks
Whenever we analyze any banking company, we’re looking at two main variables—the return a bank earns and the amount of risk. To understand any bank, you need to understand these two parameters well.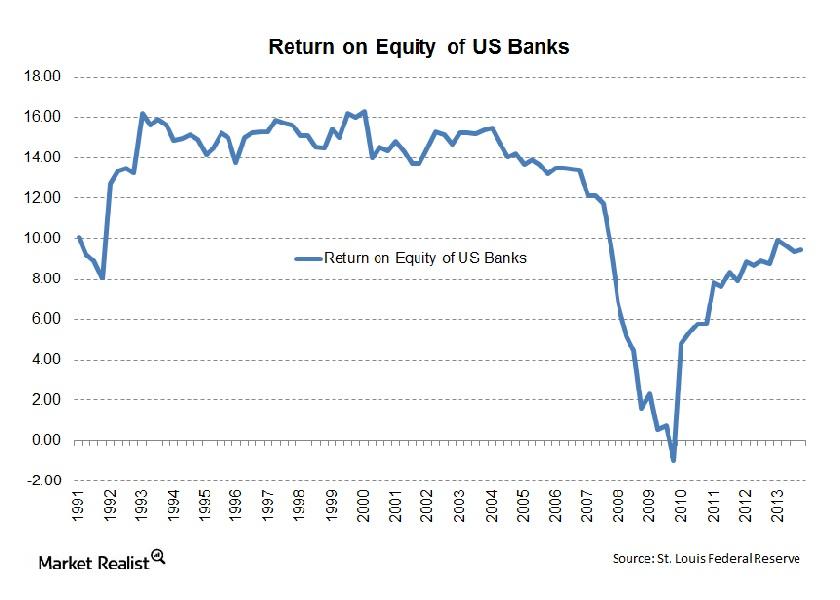
Why the price-to-book value ratio affects returns on equity
Historical analysis has shown that return on equity has a strong impact on banks’ value creation in the long run. So financials that have high price-book value ratios should also have high returns on equity.Financials Overview: What makes custodian banks different from other banks?
Custodian banks like a warehouse and store other financial institutions’ and individuals’ assets—they help in keeping financial instruments safe.
