The Full History of Google, From "Project Backrub" to Present
The timeline of the history of Alphabet Inc., best known for the Google brand, started, like many of today's biggest tech giants, with a group of Stanford students.
July 13 2022, Published 11:07 a.m. ET

Like many of the tech giants that fuel much of our daily life, Google's origin story started at Stanford University in Northern California, where a couple of Ph.D. students, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, built a search engine. A quarter of a century later, Google is so integral to the internet, it has become the verb people most commonly use when they perform a search on the internet.
Here is a comprehensive timeline of the history of Google, now officially named Alphabet. Inc., from its initial algorithm to an enormous global company that, despite its overall success, has definitely had its share of failures, too.
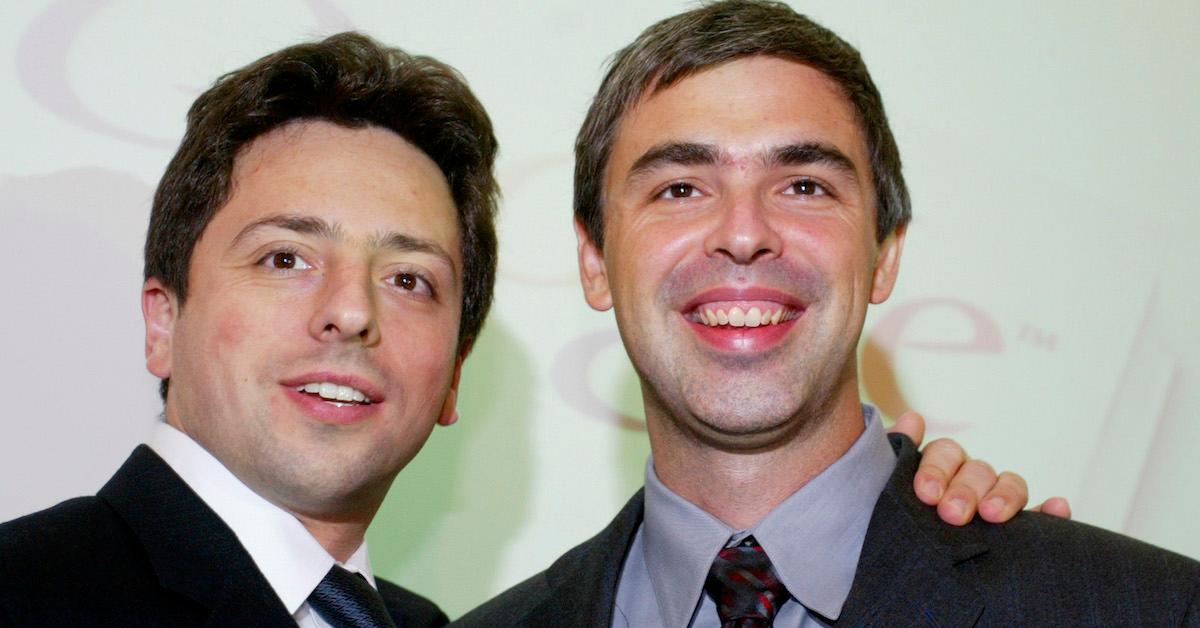

Sergey Brin and Larry Page in 2004.
1996: Larry Page and Sergey Brin started a research project nicknamed "Backrub."
The project gave birth to their Page Rank search algorithm, which uses the quantity and quality of backlinks to rank the authority of a webpage for a given search term.
September 15, 1997: Google's domain got registered.
The search engine had previously run on the stanford.edu domain. The name Google came from a misspelling of the name Page originally devised, "Googol," which is the name of the number produced when you multiple 10 to the 100th power (or a 1 followed by 100 zeroes). Arguably, it's a much better name than "Backrub" was. (Yikes.)
September 4, 1998: Google was officially incorporated.
There seems to be an unspoken rule that all great Silicon Valley companies have to be born in a garage, and in the case of Google, that garage belonged to future YouTube CEO Susan Wojcicki. The fledgling company was initially funded by a $100,000 check from Sun Microsystems co-founder Andy Bechtolsheim — probably the best $100,000 he ever spent.
Another early investor in 1998 was former Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos. Thanks to that funding round, Google was able to move out of Wojcicki's garage and into its first offices.
Early 1999: Excite turned down an offer to buy Google for less than $1M.
While many early investors saw the promise of Google, not everyone in the industry had such foresight. At one point, the now-defunct search engine Excite had the opportunity to buy Google for $1 million. One of Excite's investors even managed to talk Google down to $750,000, but CEO George Bell turned it down.
March 1999: Google moved from Menlo Park to Palo Alto.
However, Google quickly outgrew its new offices and within a few years, moved its headquarters to nearby Mountain View.
2000: Google started selling ads.
Though Brin and Page were opposed to having ads clutter the engine results, they eventually relented on the condition they were text-based so they wouldn't be too busy or cause page loads to slow. That same year, Yahoo! adopted Google as its search engine.
March 2001: Eric Schmidt became the CEO of Google.
As Google continued to grow and close several successful fundraising rounds, investors convinced Page and Brin to bring on a CEO with more experience. Eric Schmidt was previously the CEO of a software company called Novell and, before that rose through the ranks at Sun Microsystems.
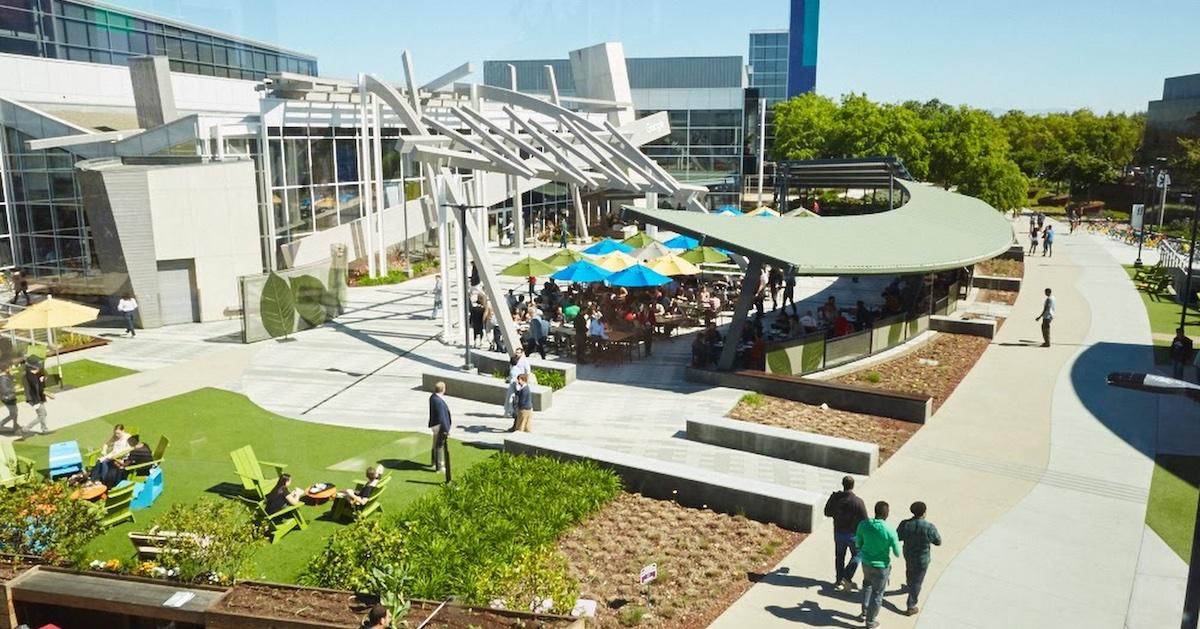

Googleplex in Mountain View, Calif.
2003: The Googleplex came to Mountain View.
Initially leasing its offices from Silicon Graphics, Google sets up in an office park in Mountain View at the site that would come to be known as the Googleplex, the company's main campus and main headquarters. The same year, Google's products expanded to include Google News. Google also acquired Blogger.
2004: Yahoo! decided to go its own way and Google went public.
After developing its own proprietary search engine, Yahoo! ended its partnership with Google, which in the short term hurt Google's value, but we all know which tech company would become a synonym for web searching. (Be honest, have you ever claimed to "yahoo" something?)
On August 19, 2004, Google went public on the New York Stock Exchange, with over $19.6 million shares initially priced at $85 apiece. As of this writing, one unit of GOOGL stock will set you back more than $2,300, though it's set to execute a 20-to-1 split on July 15, 2022.
April 1, 2004: Gmail is no joke.
Though Google would be known for its April Fool's Day pranks, the launch of Gmail was dead serious, though many thought the promised 1GB storage space was impossible. (Gmail now offers a minimum of 15 GB of storage.)

2005: Google Maps launched.
Before Google Maps, MapQuest was king, but now no other navigation software comes close to beating Google Maps in popularity (many iPhone users prefer to use Google Maps over Apple's proprietary map software.)
2006: The verb "google" was added to the dictionary and Google bought YouTube.
People had been using "google" as a verb for years, but the first significant pop culture reference to the act of searching a person's name on the engine is said to be within a Season 7 episode of Buffy the Vampire Slayer, according to Mental Floss. By 2006, Merriam-Webster and the Oxford English Dictionary made it official, though Google asked the public to only use the word when they are using Google's search engine to find information.
The same year, Google made one of its biggest acquisitions and bought YouTube for $1.65 billion on November 13, 2006. Months earlier, Google made its debut on the S&P 500. This year also brought the birth of Google Docs, Sheets, and Slides on March 9, the suite of office software that would become Google Drive and make Microsoft Office obsolete for many workplaces.
2008: The Google Chrome web browser and the first version of Android also debuted.
Google launched its proprietary browser on September 1, 2008, directly competing with Microsoft Internet Explorer and Mozilla Firefox. A month later, the smartphone operating system Android was born.

2011: Larry Page became the CEO.
Page served as the CEO of Google and, later, Alphabet until 2019, while co-founder Brin was the president of Google throughout most of that time.
June 28, 2011: Google+ debuted (and flopped).
Not everything Google touches is gold, and while certainly not the first of its products to ultimately fail, Google's attempt at building a social network, Google+, wasn't able to compete with Facebook or Twitter. The social network continued to operate until it officially ended in 2019.
2015: Google became Alphabet, Inc.
Marking a major corporate restructure, the name of Google's holding company changed to Alphabet, Inc. While Google was and continues to be Alphabet's largest subsidiary, companies under its umbrella ended up including self-driving car tech company Waymo and DeepMind, which specializes in artificial intelligence.
2018–2019: A sexual harassment scandal upset the leadership at Alphabet.
Employees started to protest the handling of sexual misconduct by leaders within Alphabet during this time, most notably Android developer Andy Rubin, who was given a cushy golden parachute after an employee made accusations against him.
Other issues that sparked walkouts and protests among employees included Alphabet's involvement in creating a censored search engine for China and providing the military with drone artificial intelligence technology. There was also growing frustration during this period with Google's over-reliance on contractors for labor. Many of those who worked full-time for the company were denied many of the famous benefits of working for Alphabet.
In response to the many controversies, workers organized several walkouts and worked to unionize Alphabet's workforces, including its contracted food service employees.
December 2019: Larry Page stepped down and named Sundar Pichai as the CEO.
Largely in response to the protests, as well as a DOJ antitrust investigation launched in June 2019, Alphabet's board seems to decide a change was needed. Page stepped down. Sundar Pichai, who had been tapped as the next CEO in 2015 when Google reorganized as Alphabet, stepped into the role for which he was anointed on December 3, 2019.
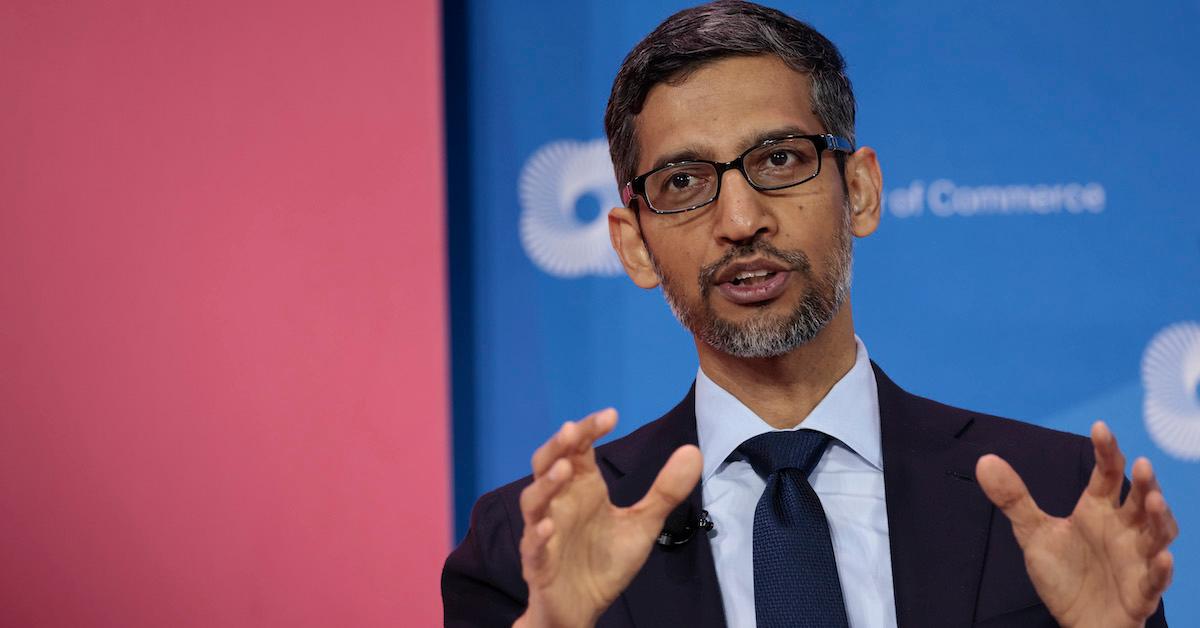

Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai
October 20, 2020: The DOJ filed an antitrust complaint against Alphabet.
The suit largely centered on Alphabet's monopolization of digital advertising, with the Justice Department arguing that the company engaged in anticompetitive practices and abused its dominance in the industry.
January 2021: The Australian government tried to get Google to compensate media companies for use of their content.
One of the many grievances made against Google is that it has increasingly made changes to the search engine to keep searchers from clicking off their site with featured snippets. These excerpts from a piece of web content are displayed at the top of search results. Many creators have complained that the practice leads essentially to them losing most of the traffic for that query to Google, since substantially fewer people will click through to read the entire article if the snippet satisfies their question.
In 2021, the Australian government proposed a law requiring Google and Facebook to compensate media companies for using their content. In response, Google threatened to pull its search engine from Australia.
