Wells Fargo & Co
Latest Wells Fargo & Co News and Updates
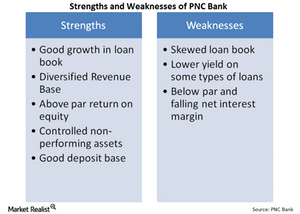
PNC Bank’s financial strengths outweigh its weaknesses
PNC Bank has done a good job at reducing its non-interest expenses, but the bank’s efficiency ratio still remains above 60%.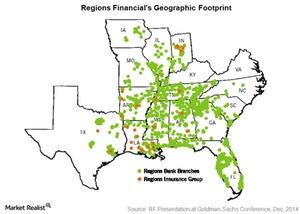
What investors should know about Regions Financial Corporation
Regions Financial Corporation is a leading regional bank in the southeastern US. It’s the 17th largest bank in the US—based on assets.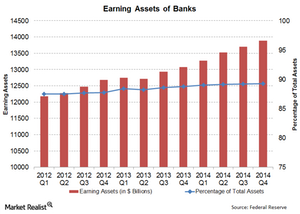
Why earning assets are an important indicator for the banking sector
The banking sector has shown a trend of increasing earning assets, because banks have focussed on becoming leaner and improving operational efficiency.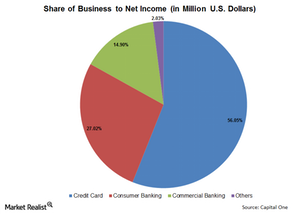
Analyzing Capital One’s business segments
Capital One (COF) can be understood best by breaking it into different business segments—Credit Card, Consumer Banking, and Commercial Banking.
What are Capital One’s three main subsidiaries?
Capital One is organized into subsidiaries. Capital One’s principal subsidiary is a limited purpose credit card bank. It’s chartered in Virginia.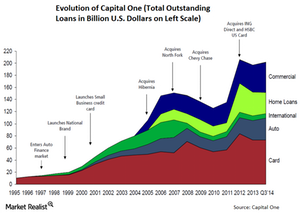
Capital One’s history: From credit cards to a diversified bank
Capital One’s history is shorter than other banks. In 1994, Signet Financial Corp. spun off its credit card business into a separate subsidiary—Capital One.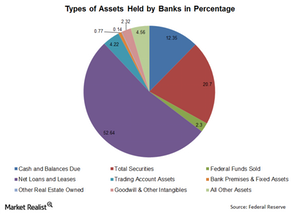
Why the composition of banking assets matters
The two main types of banking assets are loans and securities held.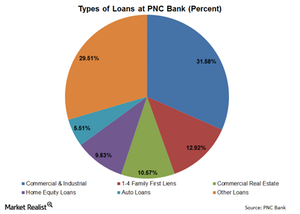
PNC Bank loan book carries some risks
PNC Bank’s loan book is skewed toward a few types of loans: commercial and industrial loans and 1–4 Family First Liens, about 44.5% of its total loans.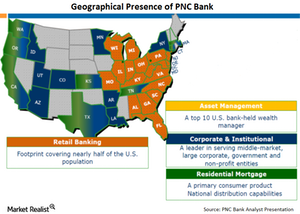
Does PNC Bank remain a strong long-term play?
With a strong presence in the East, South, and Midwest, PNC Bank offers community banking, wholesale banking, corporate banking, and asset management.
Citigroup: Number 3 US bank has $1.9 trillion in assets
Citigroup provides a broad range of financial products and services, including consumer banking, corporate and investment banking, among other things.Financials Must-know: Wells Fargo is strongly capitalized for future growth
A bank’s growth can be limited if it doesn’t have enough regulatory capital. If the bank doesn’t have enough capital, it will be forced to dilute its equity to raise capital.Financials Why Wells Fargo’s strategy is different from other banks
“Strategy” can be defined in many ways. Generally, strategy is a long-term plan. There are two main aspects to strategy—operational level strategy and human resource level strategy.Financials Why commercial lending is important to Wells Fargo strategy
The bank’s strategy is to not focus on any particular segment of industry. This helps it mitigate risk because the bank’s earnings and delinquencies are not dependent on any particular sector.Financials What are the risks associated with short-term wholesale funding?
Short-term wholesale funding refers to a bank’s use of short-term deposits from other financial intermediaries—like pension funds and money market mutual funds. It uses the short-term deposits to invest in longer-term assets—like loans to businesses. Using these short-term funds to invest in longer-term assets causes a timing mismatch between assets and liabilities.Financials Must-know: Why capital ratio is an important bank ratio
Capital ratio is also known as capital adequacy ratio or capital-to-risk-weighted assets ratio. Capital ratio is nothing but the ratio of capital a bank has divided by its risk-weighted assets. The capital includes both tier one and tier two capital.Financials Must-know: Why Basel I wasn’t a good fit for all banks
Although Basel I brought a worldwide standard in regulations, introduced the risk-weighted assets concept, and segregated capital, it had a few deficiencies.Financials Must-know: Understanding risk-weighted assets in banks
The second most important technical parameter used in banking regulations is risk-weighted assets (or RWA). If you’ve seen bank financial statements, then you might have noticed the “RWA” term there.Financials Must-know: Why capital in banking is important
Capital is important because it’s that part of an asset which can be used to repay its depositors, customers, and other claimants in case the bank doesn’t have enough liquidity due to losses it suffered in its operations.Financials Must-know: The different types of banking capital
The most important types of banking capital are common stock (or shareholders’ equity), preferred stock (or preferred equity), revaluation reserve, general provision, and hybrid instrument.Financials Overview: The basics of banking regulations
Banking regulations aim to ensure that the risks are minimized. If any unforeseen event occurs, then the interests of bank customers are protected. On a wider scale, the regulations also seek to absorb and minimize shock in the economy.Financials Must-know: The consequences of imprudent risk-taking by banks
We stated earlier that most banks are highly leveraged financial risk-takers. When things go awry, the results can be catastrophic, leading to huge losses or even to a bank closure.Financials Must-know: A thorough look at defining banking risk
Banking risk can be defined as exposure to the uncertainty of outcome. It’s applicable to full-service banks like JPMorgan (JPM), traditional banks like Wells Fargo (WFC), investment banks like Goldman Sachs (GS) and Morgan Stanley (MS), or any other financials included in an ETF like the Financial Select Sector SPDR Fund (XLF).Financials Overview: What you need to know about banking risks
Whenever we analyze any banking company, we’re looking at two main variables—the return a bank earns and the amount of risk. To understand any bank, you need to understand these two parameters well.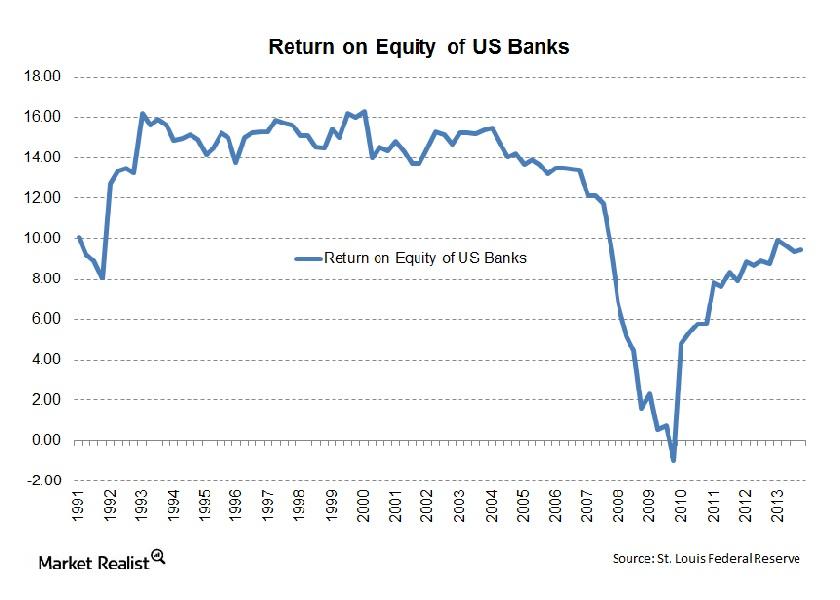
Why the price-to-book value ratio affects returns on equity
Historical analysis has shown that return on equity has a strong impact on banks’ value creation in the long run. So financials that have high price-book value ratios should also have high returns on equity.
Berkshire Hathaway reveals a new position in Goldman Sachs
Berkshire Hathaway opened a brand new position in Goldman Sachs that accounts for 2.14% of the investment company’s $104 billion portfolio.
