Trina Solar Ltd
Latest Trina Solar Ltd News and Updates
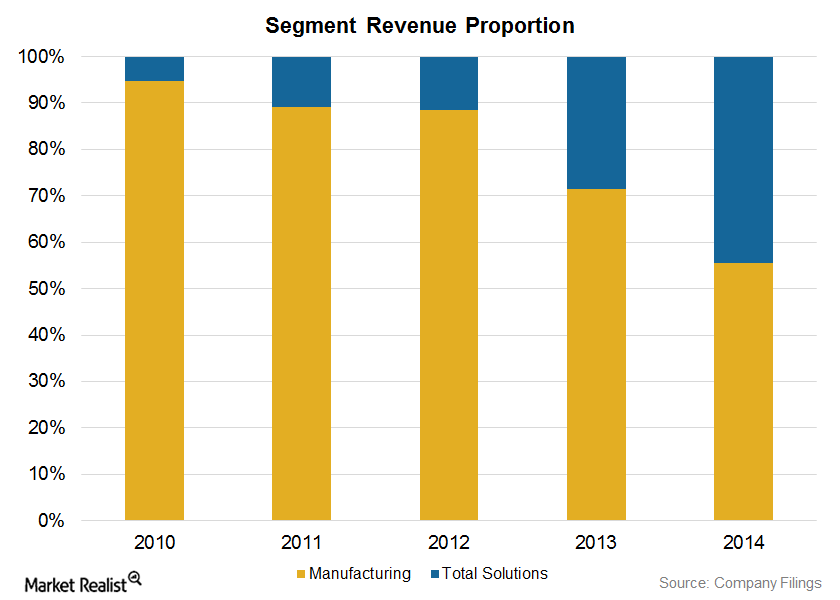
Canadian Solar’s Competitive Advantage
Canadian Solar (CSIQ) derives its competitive advantage from its strategic positioning in the downstream market, its broad range of crystalline silicon solar power products, and its technology.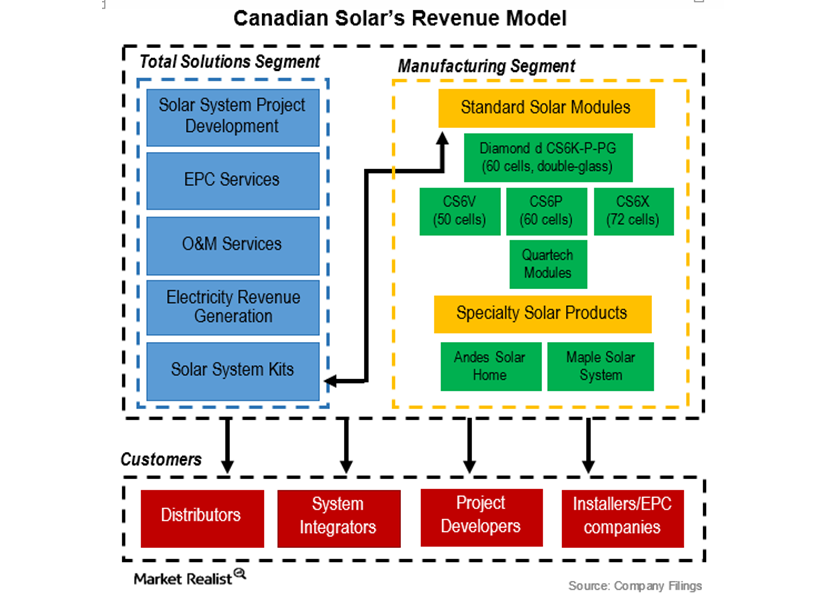
Understanding Canadian Solar’s Business Model
A significant proportion of Canadian Solar’s revenue comes from its top five customers, a structure that’s not uncommon in the industry.Industrials Coal is losing its market share in China’s electricity generation
Coal is the cheapest fossil fuel, but it’s also the most polluting. With its massive electricity generation capacity—mainly coal-fired—China emits the most carbon dioxide in the world.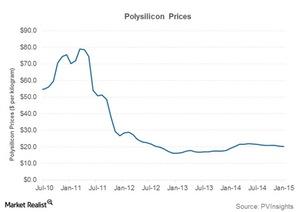
First Solar faces some must-know challenges
While First Solar has traditionally been manufacturing thin-film CdTe modules, which don’t require polysilicon, their prices have fallen in recent years.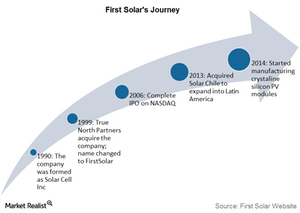
First Solar: A key player in the global solar power industry
First Solar was the first solar power company to join the S&P 500 (SPY). We’ll take a look at the company’s operations before moving on to greater details.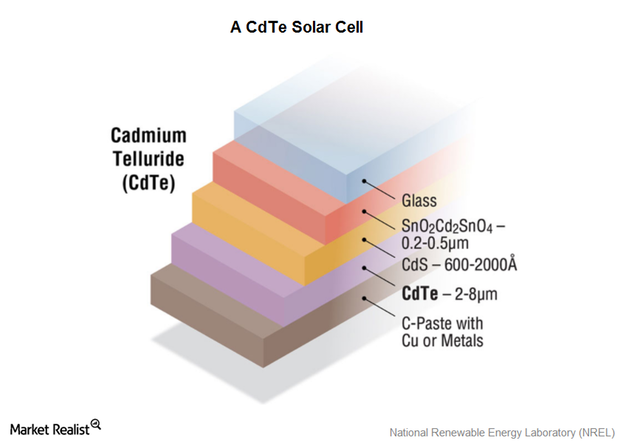
First Solar: A Key Player in the Global Solar Power Industry
First Solar (FSLR) produces solar energy equipment. In this series, we’ll look at its performance and the outlook for the industry.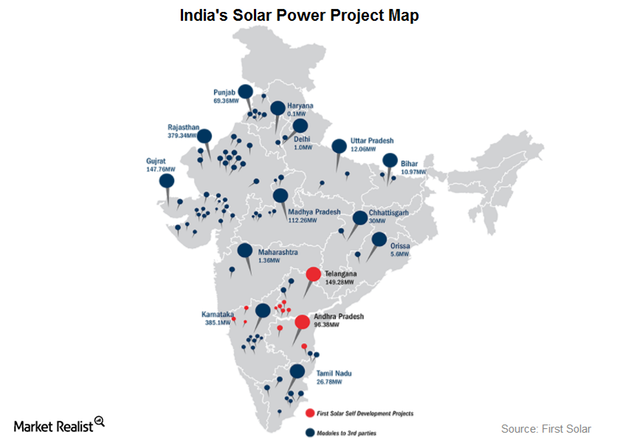
How India Became First Solar’s Second-Biggest Market
India’s rising electricity demand According to the EIA’s (U.S. Energy Information Administration) 2017 International Energy Outlook, India’s electricity generation is expected to increase by 3.2% per year through 2040, to meet increasing electricity demand in rural areas. Solar outlook Even though coal is the primary fuel used for electricity generation in India, the focus on renewable […]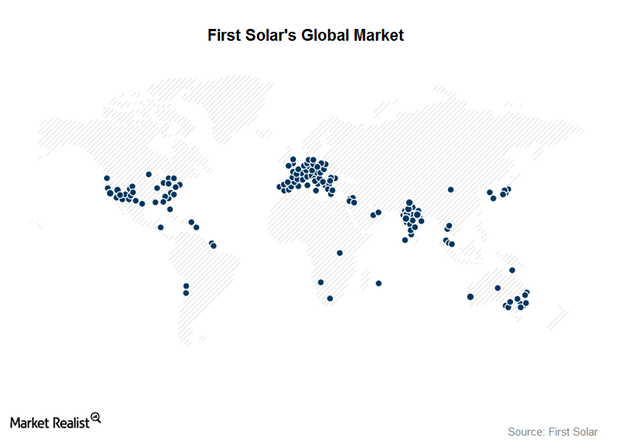
First Solar’s Global Market Strategy
The Americas The US PV (photovoltaic) market made up ~83% ($2.9 billion) of First Solar’s (FSLR) revenue. The United States has typically been First Solar’s largest market, and where many of its prominent projects and customers are located. First Solar has completed the construction of Del Sur, a 26 MW (megawatt) solar project in Honduras. It commenced […]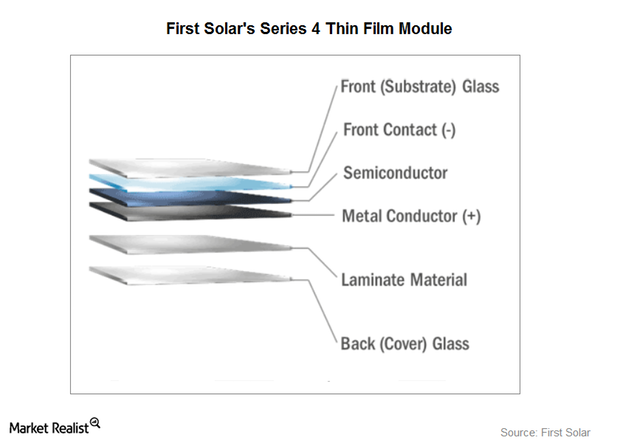
Behind First Solar’s Operations
Operating segments Previously, we looked at First Solar’s (FSLR) history. The photovoltaic module manufacturer operates two business segments: Components and Systems. The Components segment First Solar is a manufacturer of solar (TAN) photovoltaic (or PV) modules. First Solar also designs and sells these modules. They manufacture thin-film PVs, in which the semiconductor material used is […]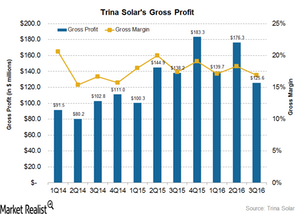
How Did Trina Solar’s Costs Affect Its Gross Margin in 3Q16?
In 3Q16, Trina Solar (TSL) reported a gross profit of $125.6 million compared to $176.3 million in 2Q16. On a YoY basis, the company’s gross profit fell nearly 9.0%.
