How Seasonality Impacts Crude Oil Prices
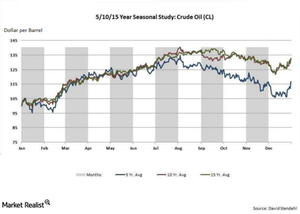
Seasonality plays a key role in influencing crude oil prices. Crude oil prices tend to rise in August due to the summer driving season, which results in a rise in gasoline demand.
April 5 2016, Updated 9:05 a.m. ET
Seasonality and crude oil prices
Seasonality plays a key role in influencing crude oil prices. Crude oil prices tend to rise in August due to the summer driving season, which results in a rise in gasoline demand. The hurricane threats in the Gulf of Mexico are also priced in during this period. But, towards mid-September and October, crude oil prices tend to peak out.
When do crude oil prices bottom out?
Crude oil prices tend to fall during early October due to sluggish demand in the winter. Price analysis of crude oil projects suggests that crude oil prices generally peak between September and October. Then prices start to make lower highs between October and November. Finally, they hit the bottom by December.
Seasonality influences crude oil prices under normal supply and demand conditions. But compared to geopolitical tensions, oil glut, economic slowdown, or a financial crisis, the seasonality factor could have a minor effect.
Stocks and ETFs
Crude oil prices affect ETFs and ETNs like the ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Crude Oil ETF (SCO), the United States Oil Fund (USO), the PowerShares DWA Energy Momentum (PXI), the United States Brent Oil (BNO), and the United States 12 Month Oil (USL). They also influence national and international oil companies like CNOOC (CEO), China Petroleum & Chemical (SNP), Comstock Resources (CRK), Northern Oil & Gas (NOG), and Triangle Petroleum (TPLM).
Read the next part of the series to know more about fund flow into commodities.
