How Global Gross Domestic Product Affects Crude Oil Prices
The IMF (International Monetary Fund) forecasts that the world economy will grow by 3.4% in 2016 and 3.6% in 2017.
March 1 2016, Published 8:01 a.m. ET
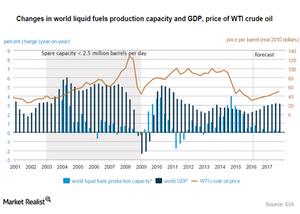
Global GDP and crude oil prices
The chart below shows that whenever the global GDP (gross domestic product) has increased, crude oil prices have rallied. This suggests that during periods of economic growth, crude oil demand has risen and supported crude oil prices. In contrast, lower economic growth led to the fall of crude oil prices in 2008 and 2009.
Global GDP estimates
The IMF (International Monetary Fund) forecasts that the world economy will grow by 3.4% in 2016 and 3.6% in 2017. In contrast, the World Bank estimates that the world economy will grow by 3.3% in 2016 but decline by 3.2% in 2017. Economic growth would be driven by emerging economies in 2016 and 2017. However, the slowing Chinese economy will put pressure on oil prices and global markets.
Impact
The volatility in the global markets, the slowing Chinese economy, and mixed global growth data will put pressure on crude oil prices. Oil prices are expected to be volatile in 2016 and 2017. The volatility in oil prices affects oil producers like Devon Energy (DVN), Laredo Petroleum (LPI), Chesapeake Energy (CHK), Range Resources (RRC), and Pioneer Natural Resources (PXD). Volatile oil prices also influence US refiners such as Western Refining (WNR), Alon USA Partners (ALDW), Tesoro (TSO), and Northern Tier Energy (NTI).
To diversify exposore to oil and gas companies, you can invest in ETFs and ETNs such as the VelocityShares 3x Inverse Crude Oil ETN (DWTI), the Vanguard Energy ETF (VDE), and the iShares U.S. Energy ETF (IYE).
