How Could the Novartis-Xencor Alliance Benefit Novartis?
As we’ve discussed, Novartis (NVS) is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies by revenue.
July 6 2016, Updated 10:19 a.m. ET
About Novartis
As we’ve discussed, Novartis (NVS) is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies by revenue. Its headquarters are in Basel, Switzerland. The company specializes in the research, development, manufacturing, and marketing of a broad range of healthcare products. The company deals in both prescription drugs as well as over-the-counter drugs.
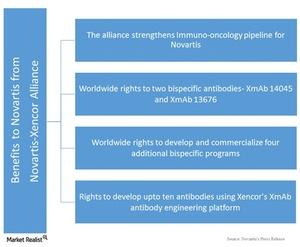
The Novartis-Xencor alliance
The Novartis-Xencor alliance is focused on the codevelopment of two bispecific antibodies, as well as licensing Novartis to use Xencor’s XmAb Bispecific Fc Domain technology for developing new antibodies. According to the terms of the agreement, Novartis gets the following rights:
- worldwide rights for codeveloping two T-cell-engaging bispecific antibodies, XmAb 14045 and XmAb 13676, with development costs being borne equally by Novartis and Xencor
- commercialization rights for these two bispecific antibodies for outside US markets
- rights to develop and commercialize four additional bispecific programs worldwide
- Novartis receives the right to use Xencor’s XmAb antibody engineering platform for developing up to ten additional antibodies
Xencor will receive an upfront payment of $150 million, plus tiered royalties. We’ll discuss this in the next article.
XmAb 14045
XmAb 14045 is a tumor-targeted antibody designed for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (or AML) and other hematologic malignancies. XmAb Bispecific Fc Domain attaches two antigen binding domains—the CD123 binding domain and the cytotoxic T-cell binding domain. The compound XmAb 14045 is stable, easy to manufacture, and the technology also grants a long half-life. With the use of XmAb Bispecific Fc Domain, controlled T-cell activation helps kill CD123-expressing tumor cells and balance anti-tumor activities by reducing immunotoxicity due to T-cell activation.
XmAb 13676
XmAb 13676 is a tumor-targeted antibody designed for the treatment of B-cell malignancies. XmAb Bispecific Fc Domain attaches two antigen binding domains—the CD20 binding domain and the cytotoxic T-cell binding domain. The compound XmAb 13676 is stable, easy to manufacture, and the technology also grants a long half-life. With the use of XmAb Bispecific Fc Domain, controlled T-cell activation helps kill CD20-expressing tumor cells and balance anti-tumor activities by reducing immunotoxicity due to T-cell activation.
Drugs approved for the treatment of leukemia include Amgen’s (AMGN) Blincyto, Sanofi’s (SNY) Clolar, Ariad Pharmaceuticals’ (ARIA) Iclusig, Bristol-Myers Squibb’s (BMY) Sprycel, and Novartis’s Gleevec.
To divest risk, investors could consider ETFs such as the PowerShares International Dividend Achievers ETF (PID). 1% of its total assets are in Novartis.
