What Is Labor Market Slack?
The unemployment rate doesn’t help us gauge the extent of labor market slack. The actual employment gap that exists also consists of a slack component.
March 11 2016, Updated 2:05 p.m. ET
The employment gap
Conventionally, employment gap has been simply defined as the difference between the unemployment rate and the natural rate of unemployment. The natural rate of unemployment is the rate consistent with full employment, the rate at which the economy can tread on a balanced growth path. Monetary authorities tend to look at this gap when assessing the need for further monetary policy action to bridge the gap.
Slack is often overlooked
However, this view needs to be broader. The unemployment rate doesn’t help us gauge the extent of labor market slack. The actual employment gap that exists also consists of a slack component. Below are the two primary components of slack:
- underemployment: people working part-time who want a full-time job
- hidden unemployment: people who are not actively searching but who would rejoin the workforce if the job market were stronger
For the United States (VFINX) (SPXL), labor market deficiencies include the following:
- unemployment: part of the total labor force that’s unemployed currently but is actively seeking employment and is willing to work
- hidden unemployment: marginally attached workers or discouraged workers
- underemployment: people who are working part-time for economic reasons (or PTER)
Hidden unemployment
Hidden unemployment can be looked at as the participation gap. Participation gap is the difference between the actual size of the labor force versus assessments of a potential labor force. For example, a stay-at-home mom may be thinking of returning to the workforce. However, until the wage level adequately covers the cost of her child’s daycare, this marginally attached worker would prefer to stay home.
Underemployment
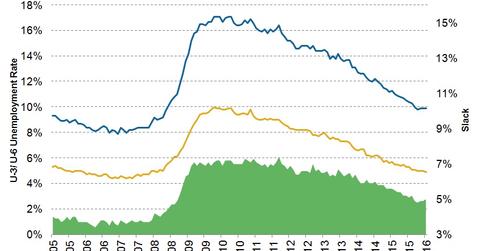
Underemployment accounts for those people who are working PTER. The U-6 measure of unemployment accounts for the marginally attached and the PTER workers. The difference between the U-3 (headline unemployment rate) and the U-6 unemployment rate gives a fair idea of labor market slack.
Considering that the US (SPY) (IWM) (QQQ) Federal Reserve is bound by its dual mandate of attaining full employment along with price stability, wage growth and its impact on inflation becomes critical for the Fed. In fact, wage inflation is one aspect that definitely has a critical role in the Fed’s decision-making process at its monetary policy meetings.
Next, let’s see what makes wage inflation so critical.
