Underwriting cycle: What health insurance investors need to know
The underwriting cycle results from the uncertainty of predicting healthcare expenses and the fluctuating participants in the health insurance industry.
Feb. 12 2015, Updated 11:05 a.m. ET
Underwriting cycle
The health insurance industry (XLV) accepts the responsibility for paying covered individuals’ medical bills in exchange for a specified amount of money, payed periodically, called “premiums.” This is known as “underwriting.” When the total premiums earned by the industry exceed the total money paid for medical bills and administrative expenses, the profit is called the “underwriting gain.” When expenses exceed the total earnings, they’re called the “underwriting loss.” The underwriting cycle results from the uncertainty of predicting healthcare expenses and the changing number of participants in the health insurance industry.
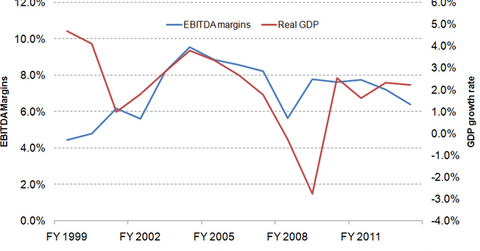
The above graph shows the average earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (or EBITDA) margin of the private health insurance industry, calculated as an average of the EBITDA margins of Aetna (AET), Humana (HUM), Cigna (CI), UnitedHealth Group (UNH), Molina Healthcare, Centene, and Anthem. You can see that the average earnings change according to business cycles, increasing in periods of economic growth and declining in periods of recession.
Competitive environment
Premium rates are set up in advance of the coverage period based on projected healthcare costs. However, healthcare costs abruptly increase, health insurers face losses as expenses exceed earnings. In response, health insurers raise premiums to make up for past losses. When the total premiums exceed the total healthcare costs and administrative expenses of the health plan, high profits attract many new players to enter the market.
New firms have easy access to capital in economic booms. Also, as more people can afford health insurance during times of economic health, new companies’ entry generally coincides with economic booms. Increasing competition puts downward pressure on premiums, reducing profits. Also, in recessions, unemployment increases and people are unable to afford health insurance, further stressing revenue and leading to insurers exiting the market.
