What Are Lowe’s Supply Chain and Inventory Management Policies?
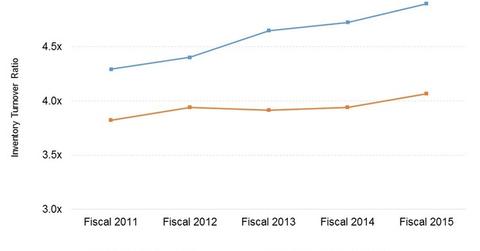
Lowe’s inventory turnover came in at 4.1x in fiscal 2015 compared to 4.9x for Home Depot (HD).
Nov. 20 2020, Updated 5:20 p.m. ET
Where Lowe’s sources its products from
Lowe’s sources its products from over 7,000 vendors. Suppliers include large companies like General Electric (GE) and Samsung (SNNLF) for appliances, as well as power tools suppliers like Dewalt, and paints and coatings suppliers like Valspar (VAL) and Sherwin-Williams (SHW). None of its suppliers account for over 10% of purchases, so the suppliers’ individual impact on the company’s performance is limited.
Supply chain network
80% of the company’s purchases were shipped via its distribution network in fiscal 2015. The company’s US distribution network consists of 15 regional distribution centers (or RDCs), each of which serves about 115 stores. Besides, Lowe’s also tries to purchase merchandise directly from manufacturers to cut down the layers in the distribution network and pass on the resultant savings to customers in the form of lower prices.
Inventory management
Each Lowe’s store stocks approximately 36,000 items. However, Lowe’s has several hundred thousand items on tap for its customers, which can be ordered via its e-commerce sites, and its special sales order system. This enables the company to optimize its inventory between stores and distribution centers.
Lowe’s inventory turnover came in at 4.1x in fiscal 2015 compared to 4.9x for Home Depot (HD). Lowe’s is aiming for faster inventory turns with a target ratio of 4.4x in fiscal 2016. In comparison, other big box retailers like Walmart (WMT) and Costco (COST) achieved inventory turnover ratios of 8.1x and 11.6x, respectively, in their last fiscal years. The differential merchandise mix has been primarily responsible for higher inventory turns for both Walmart and Costco.
LOW, HD, SHW, WMT, and COST together constitute 2.4% of the portfolio holdings in the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO).
