An Overview of Biogen’s Business Model
A leader in the development of multiple sclerosis treatments, Biogen earned 82.5% of its total revenues from its MS drugs in 2014.
July 23 2015, Published 11:47 a.m. ET
Biogen’s business model
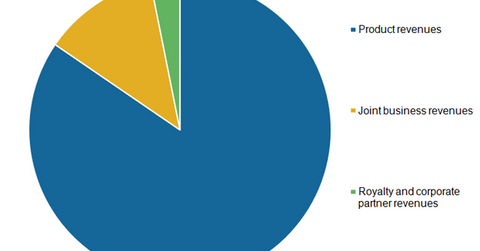
Biogen (BIIB) generates revenues in three ways: product revenues, revenues from joint businesses, and royalty and corporate partner revenues.
Product revenues
Considered to be an industry leader in the development of multiple sclerosis (or MS) treatments, Biogen earned 82.5% of its total revenues from its MS drugs in 2014. According to WebMD, “Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a long-lasting disease that can affect your brain, spinal cord, and the optic nerves in your eyes. It can cause problems with vision, balance, muscle control, and other basic body functions.” Biogen relies heavily on its three blockbuster MS drugs: Avonex, Tecfidera, and Tysabri.
However, Biogen aims to lower its excessive dependence on MS and has been introducing drugs in other therapeutic areas. The company introduced two drugs to treat hemophilia, a condition where blood does not clot properly. In March 2015, Biogen announced that its experimental Alzheimer’s disease drug has proved highly successful. Analysts expect that the drug can enter the market by 2018.
Joint business revenues
Biogen has collaborated with Genentech for the development and commercialization of the drug Rituxan. Rituxan is used to treat conditions related to lymphoma, leukemia, organ transplants, and autoimmune disorders. In addition, Biogen shares its profits and losses with Genentech relating to the sales of its drug Gazyva, a drug for chronic leukemia, in the US. In exchange, Genentech is responsible for all the costs related to further development and commercialization of Gazvya.
Royalty and corporate partner revenues
Biotechnology companies such as Amgen (AMGN), Biogen, Celgene (CELG), and Gilead (GILD) also earn revenues from licensing arrangements. In a licensing arrangement, a biotechnology company generally transfers its patented drug technology to a larger biotechnology or pharmaceutical company in exchange of an upfront payment called a license fee.
In addition, the seller may require the buyer to pay a fixed percentage of its sales or profits from the commercialization of its transferred drug technology. This is referred to as a royalty. Biogen’s royalty revenues are mainly derived from its worldwide sales of Angiomax, licensed to The Medicines Company, and the royalties are tied to the drug’s total sales in a year.
Biogen also entered into a joint venture with Samsung Biologics to develop biosimilars or generic biotechnology drugs for big pharma companies on a contract basis. With the growth in the biosimilar market, these revenues, termed as corporate partner revenues, are expected to rise significantly.
Investors can get exposure to Biogen’s business while protecting themselves against excessive company-specific risks by investing in the iShares NASDAQ Biotechnology ETF (IBB). IBB holds 7.48% holdings in Biogen stock.
