The Business Models of Biotechnology Companies
The type of business model a biotechnology company selects depends on technical capability, availability of resources, and competition in the industry.
July 3 2015, Updated 10:06 a.m. ET
Business models
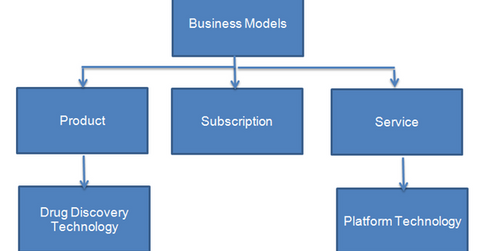
Based on the nature of what’s being marketed, biotechnology companies (IBB) can be segmented into three categories: product companies, subscription companies, and service companies. The type of business model a biotechnology company selects depends on technical capability, availability of resources, and competition in the industry.
Product companies
The product-based category is the dominant business model in the biotechnology industry. In this category, the company develops drugs and sells them in the market. Product companies are mainly involved with drug discovery. These companies focus mainly on developing drugs for a particular class of disease. In addition to marketed drugs, these companies generally have several drugs in various phases of the drug approval process.
Companies such as Amgen (AMGN), Biogen (BIIB), Celgene (CELG), and Regeneron (REGN) enter into partnerships or collaborative arrangements with other biotechnology companies or large pharmaceutical companies to share the risk and rewards of drug discovery.
Subscription companies
Subscription-based companies such as Celera and Gene Logic develop genome databases, which can be used to develop medicinal drugs. Pharmaceutical companies subscribe to the data and pay subscription fees to these companies.
Service companies
The majority of service companies in the biotechnology sector are platform technology companies. Platform technology companies offer solutions based on a common technology or generic tool of other large pharmaceutical or biopharmaceutical companies. Examples include companies like Qiagen, which provides software solutions for biological data analysis, and Affymetrix, which offers micro-array technology used to analyze hereditary material in the body.
Contract research organizations (or CROs) also form a major part of service-based biotechnology companies. A large pharmaceutical company outsources its research and development activities to a CRO on a contract basis. Other service-based companies support the preclinical, clinical, regulatory, manufacturing, marketing, distribution, and commercialization functions of large pharmaceutical companies.
