OPEC’s Role in World Oil Production
OPEC (the Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) aims to “coordinate and unify the petroleum policies of its Member Countries.”
April 30 2019, Published 2:41 p.m. ET
OPEC countries
OPEC (the Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) aims to “coordinate and unify the petroleum policies of its Member Countries” to ensure:
- “the stabilization of oil markets in order to secure an efficient, economic and regular supply of petroleum to consumers”
- “a steady income to producers”
- “a fair return on capital for those investing in the petroleum industry”
Currently, OPEC has 14 member countries.
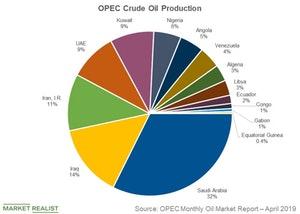
OPEC’s contribution to world oil production
OPEC supplies around 30% of the world’s total oil production. As the above graph shows, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and Iran are the biggest contributors to the OPEC supply. Saudi Arabia is the second-largest producer, followed by the United States.
Imports and exports
Even though the United States is the largest producer of crude oil (USO) in the world, it’s a net importer of oil because it’s the largest oil consumer, too. According to OPEC’s “Oil Market Report” for April, the United States total net imports of crude oil and products averaged 1.1 million barrels per day in March. The EIA projects that, by 2020, the country will export more petroleum and other liquids than it imports.
China and India, the top oil consumers after the United States, are also net importers of oil. On the other hand, Saudi Arabia, Russia, and Canada are net exporters. ConocoPhillips (COP), EOG Resources (EOG), Occidental Petroleum (OXY), and Apache (APA) are among the top oil and gas exploration and production companies in the United States.
