Fertilizers: A Key Part of Increasing Crop Yields
Increasing crop yield on available farmland could be the best solution to the problem of increasing crop production.
Jan. 13 2017, Published 8:17 a.m. ET
Crop production solutions
We’ve already seen how global food consumption per person per day has increased over the years and is expected to rise in the future. To meet the need for growing food consumption, there has to be an increase in crop production.
The FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) offers three solutions to increase crop production:
- expand the area of land
- increase crop planting frequency
- increase yields
Farming challenges
Land is a finite resource and thus limits the growth prospects for making drastic increases in arable land. Similarly, planting seasons have limited days, which limits the increase in planting frequency. For example, corn grows when the weather is suitable and takes about 60–100 days to be ready for harvest.
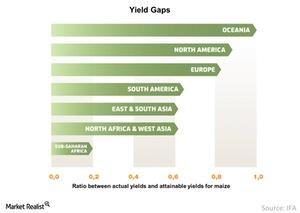
The above graph shows the ratio between actual yields and attainable yields for corn around the world. Sub-Saharan Africa’s actual yield is only one-fifth of its total attainable yield. Oceania’s actual yield is very close to its full attainable yield. So increasing crop yield on available farmland could be the best solution to the problem of increasing crop production.
Increasing yields
A document titled “Mineral Fertilizer Use and the Environment,” published by the IFA[1. International Fertilizer Industry Association] and UNEP,[2. United Nations Environment Programme] states, “Amongst the various agricultural inputs, fertilizers, perhaps next only to water, contribute the most to increasing agricultural production.”
The above picture shows the visible impact of using fertilizer to increase crop production or yield.
PotashCorp (POT), Agrium (AGU), Mosaic (MOS), and CF Industries (CF) are some of the largest manufacturers of fertilizers (XLB). Let’s dig more deeply now and see how fertilizers impact crop production.
