What Problems Is Apple Facing in China?
Apple’s problems in China seem to have worsened in the last few weeks.
June 30 2016, Updated 10:07 a.m. ET
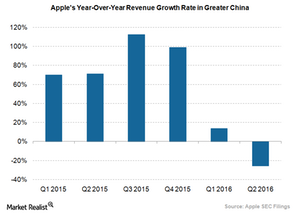
Apple’s Chinese revenues decline
China has started to become the most important market for Apple (AAPL) after the United States. About 25% of its revenues came from the Greater China (China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan) market last quarter, only behind the Americas market, which accounted for 38% of its revenues. Apple continues to invest heavily in China. The company opened seven retail stores in the last quarter, reaching a total of 35. Apple plans to open another five stores this quarter.
However, behind these seemingly strong numbers, Apple is facing a number of problems in China. To start with, it had negative revenue growth in Greater China last quarter, whereas we are used to seeing strong growth. The chart above shows that the year-over-year revenue growth in Greater China in the last quarter was -26%, while this growth was in excess of 70% in each of the quarters of fiscal 2015. Apple blamed this negative growth on weakness in Hong Kong due to the strong US dollar, but the growth in Mainland China was still negative at 11%.
Apple’s problems in China have worsened
In April this year, Apple’s iBooks and iTunes were banned from China (FXI) because the company didn’t have the required licenses. More recently, China ordered Apple to stop selling the iPhone 6 and iPhone 6 Plus in China due to a patent infringement issue. These issues prompted billionaire activist investor Carl Icahn to exit his Apple investments.
In the past, China hasn’t been friendly to foreign technology (QQQ) companies. Microsoft (MSFT) and Qualcomm (QCOM) are prominent examples. Last year, Qualcomm settled an antitrust claim by paying a fine of $975 million to the Chinese government.
