Company Overview: An Introduction to Casey’s General Stores
Casey’s General Stores’ strong and differentiated business model has resulted in the company’s delivering total returns of 27% in the last year.
April 18 2016, Published 2:56 p.m. ET
Snapshot
Casey’s General Stores’ (CASY) strong and differentiated business model has resulted in the company’s stock outperforming its peers. While CASY has delivered total shareholder returns of 27% over the last year, CST Brands (CST) and Murphy USA (MUSA) have registered returns of -11.7% and -15%, respectively, over the last year.
CASY has been able to take full advantage of falling gas prices by effectively diverting the extra spending of its customers to its prepared food and grocery segments. The company has taken several profit-boosting initiatives, such as adding a pizza delivery service and converting stores into a 24-hour format over the last couple of years.
As a result, Casey’s registered a 42% year-over-year (or YoY) rise in net income during 2015. Nonetheless, volatile fuel prices took a toll on Casey’s profitability in fiscal 3Q16, and the company saw a 4% fall in its earnings per share on account of a ~20% fall in the retail price of fuel.
Business overview
Casey’s, along with its subsidiaries, operates 1,908 convenience stores in 14 Midwestern states, with strong presences in Iowa, Missouri, and Illinois. Casey’s stores are mostly located in areas with low population density.
Approximately 57% of the company’s stores are located in areas with populations of fewer than 5,000 people. The company owns most of its assets and operates its own distribution centers, which provide ~75% of the gasoline and ~90% of the products sold in its stores.
Investors looking for exposure to Casey’s can invest in the iShares Russell 2000 Growth ETF (IWO), which has around 0.53% of its holdings invested in the company.
Financial performance
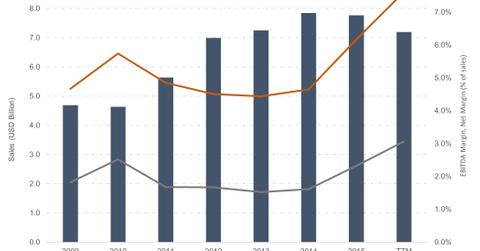
Casey’s fiscal 2015 (for the year ending April 30, 2015) sales stood at $7.8 billion. While a third of this revenue came from selling grocery, merchandise, and prepared foods, around 66% of it was attributable to gasoline sales.
The company’s revenues grew at a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 11% between fiscal 2010 and fiscal 2015. While its in-store sales have risen by an average of 12% during the last five fiscal years, its gasoline sales have been quite volatile due to unstable fuel prices. In-store sales, which account for around 33% of the company’s revenue, generated about 77% of its gross profit in fiscal 2015.
Competition
The company competes with other convenience store chains such as CST Brands, 7-Eleven, Quiktrip, Kwik Trip, and Alimentation Couche-Tard. It competes with gas station chains such as Murphy USA, supermarkets such as Kroger (KR), and mass merchants such as Walmart (WMT) and Costco (COST).
In this series
In this series, we’ll provide a business and financial overview of Casey’s General Stores and its operations. We’ll aim to understand the company’s business model, and we’ll take a look at its strategies. We’ll also analyze the company’s key growth drivers, its past financial performance, and its sources of future upside for investors. In the end, we’ll take a quick look at the company’s stock returns and valuations versus those of its peers.
