Where Are the Low Sulphur Content Coal Mines in the US?
According to the EIA, low sulphur content coal is defined as having less than 0.60 pounds of sulphur per million British thermal units.
Feb. 9 2016, Published 2:49 p.m. ET
Classification of coal by sulphur content
According to the EIA, low sulphur content coal is defined as having less than 0.60 pounds of sulphur per million British thermal units (or MMBtu). Medium sulphur content coal has 0.61-1.67 pounds of sulphur per MMBtu, and high sulphur content coal has more than 1.67 pounds of sulphur per MMBtu.
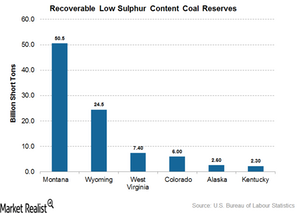
Geographic distribution
Montana has the largest deposits of low sulphur coal of any state in the US, followed by Wyoming, West Virginia, and Colorado. Almost all of the low sulphur content coal is confined to the Western US. As we discussed in part three of this series, the geologic age of coal formation is one of the key factors that defines the characteristics of coal available in these regions.
Although Montana has the largest deposits of low sulphur content coal, due to environmental concerns and poor quality of coal available, it is not among the top coal-producing states in the country.
Major coal producers in the West
According to the EIA, North Antelope Mine, owned by Peabody Energy (BTU), and Black Thunder mine, owned by Arch Coal (ACIIQ), together produced about 22% of the total coal mined in the US in 2013. Coal produced from these mines has low sulphur content according to EIA’s standards. Cloud Peak Energy (CLD) and Alpha Natural Resources (ANRZQ) are other major coal (KOL) producers in this region.
What are the different mining methods in the three major coal mining regions of the US? Let’s look at this in the next part of the series.
