A Look at the Courier Service Industry in the United States
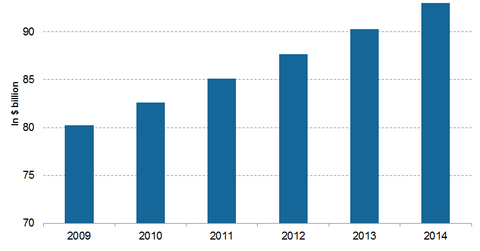
The growth in e-commerce among various economies across the globe has helped shape the highly competitive courier service industry that we know today.
July 17 2015, Published 9:12 a.m. ET
Overview
The couriers and local delivery services in the US primarily provide express delivery and pickup of parcels. The industry transports goods that are non-palletized and weigh less than 110 pounds. The industry is divided into two segments:
- large networked couriers capable of nationwide and international delivery
- smaller local services that transport packages within a metropolitan area
Online consumer spending and business transactions are the two major demand drivers. The profitability of individual companies is driven by reliability, price, services, and quality. Large companies compete by offering a wide range of services. Small companies compete through specialized customer service.
Competition
The United States Postal Service is the only government-owned player in the industry, which is primarily dominated by local private players such as United Parcel Services (UPS) and FedEx (FDX), as well as other companies such as Deutsche Post DHL in Germany and TNT in the Netherlands. The industry is characterized by high shipping volumes, low weights, and timely delivery of shipments.
FedEx forms 2.18% of the PowerShares Buyback Achievers ETF (PKW). Other companies included in the ETF are Expeditors International (EXPD) and Allegiant Travel (ALGT) with 0.4% and 0.14% holdings, respectively.
Capital intensity
The industry is both capital-intensive and labor-intensive. Labor expenses include the wages and salaries paid to drivers, pilots, operators of call centers and drop-off locations, ground and administrative staff, and loading crews. As Western operators initially cut back in capital investments amid the global economic slowdown, the capital intensity has fallen in the past five years.
A brief history
The package delivery industry has changed dramatically over the years. The earliest known private express company was Wells Fargo, which was founded in 1852. During that time, the industry was unregulated and packages were delivered manually from door to door. However with the passage of time, the industry has adapted technologically and now makes use of sophisticated equipment and networks to ensure fast and timely delivery. Globalization and the growth in e-commerce among various economies across the globe has helped shape the highly competitive courier service industry that we know today.
