Home Depot Sales Likely to Be Influenced by Macroeconomic Factors
The US Federal Reserve dialed down its outlook for economic growth in 2015. Slower growth may affect sales performance at Home Depot (HD) this fiscal.
April 9 2015, Updated 4:04 p.m. ET
Macro factors influencing revenues
The home improvement retail (XRT) industry is highly cyclical. The industry benefits when the economy is on an uptrend and employment levels are healthy. Consumer income and spending trends are critical to the performance of the consumer discretionary (XLY) sector, which includes home improvement retailers such as Home Depot (HD), Lowe’s (LOW), Williams-Sonoma (WSM), Bed Bath & Beyond (BBBY), and Restoration Hardware (RH).
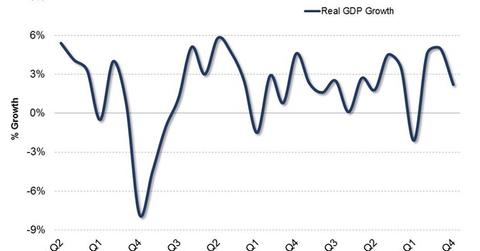
Gross domestic product
The percentage change in GDP (gross domestic product) measures the rate at which the economy is growing. Real GDP grew 2.4% in 2014, up slightly from 2.2% in 2013.
At its March, 2015 Federal Open Market Committee, or FOMC, meeting, the US Federal Reserve dialed down the outlook for US economic growth in 2015 from between 2.6% and 3% to between 2.3% and 2.7%. Slower growth is primarily due to the appreciating US dollar that’s affecting the exports component of GDP as well as slow growth overseas that’s affecting results for US businesses with overseas operations. It’s also due to a weak consumer spending environment, which we’ll look at in the next article of this series.
Impact on home improvement retailers
Slower growth may affect sales performance at Home Depot (HD) in the current fiscal. HD expects US same-store sales to grow at 1.5% over the GDP growth rate. In its fiscal 2015 earnings release, HD projected 3.3% to 4.5% comps growth in fiscal 2016—that is, this year. A slower growth forecast may mean lower sales growth for HD.
Lowe’s is projecting growth of 4% to 4.5% in store comps this year. Lower GDP growth and consumer spending may affect sales projections for both retailers.
