Traditional assets: Defining active and passive management
Active asset management refers to those asset managers that essentially try to outperform the average market return, a benchmark, or a hurdle rate that may have been set internally.
Nov. 20 2020, Updated 12:47 p.m. ET
Asset management requires expertise
Managing financial assets requires expertise in at least one of these areas:
- Equities
- Fixed income – popularly called bonds
- Commodities
- Real estate
- Foreign exchange
It’s difficult for a non-professional to invest financial assets and get the desired return, either due to a lack of expertise or a lack of time.
Asset management is divided into two broad categories:
- Traditional asset management
- Alternative asset management
Traditional asset management, as the name suggests, is made up of simple strategies involving the purchase of securities only. This style of management is the focus of this series.
Two main types of traditional asset managers
Every industry has an inherent structure determined by the environment in which it operates and the competencies it requires. In an overview series on the banking sector, we learned that banks can be classified according to three main types. Similarly, traditional asset management has two main types:
- Active asset management
- Passive asset management
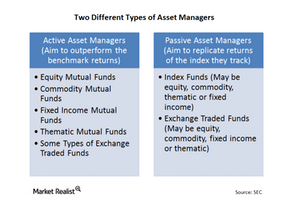
Active asset management: Trying to do better than the average
Active asset management refers to those asset managers that essentially try to outperform the average market return, a benchmark, or a hurdle rate that may have been set internally.
Passive asset management: Trying to replicate the benchmark
Passive asset management refers to those asset managers that don’t try to outperform the average market return or benchmark. Instead, the goal is to replicate the average market return or benchmark.
Many asset managers focus their investment strategies on a single asset class, like Janus (JNS) does with equities or fixed income, for example. Some focus on a style of investing, like BlackRock (BLK) and State Street (STT). Some big banks, such as JP Morgan Chase & Co. (JPM), and investment banks, such as Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley, which are part of the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY), focus on active asset management. Other managers cover broad market areas, offer multiple strategies within a fund or family of funds, and provide custom investment services for clients.
