Fertilizer industry overview: Must-know fertilizer types
Fertilizers are used in the agriculture industry to improve the yield farmers receive. The three main types of nutrients or fertilizers are nitrogen, phosphate, and potash.
Oct. 16 2013, Published 12:51 p.m. ET
Fertilizer types
Fertilizers are used in the agriculture industry to improve the yield (the amount of crop) farmers receive from an acreage of land. The three main types of nutrients or fertilizers are nitrogen, phosphate, and potash—with nitrogenous fertilizer industry being the largest fertilizer type, followed by phosphate and potash.
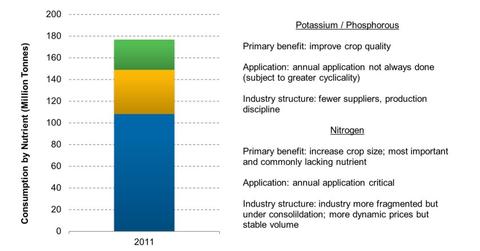
Nitrogen: 108 million tonnes of consumption
Urea, UAN, and ammonia are common products that fall under the category of nitrogenous fertilizers. These fertilizers must be applied every year to maintain yield and biomass, and they’re essential for growth and development in plants. Deficit application of nitrogen can negatively affect plant growth, vigor, color, and yield. As farmers have to apply them every year, demand for nitrogenous fertilizers tends to be more price-inelastic. This means farmers aren’t going to change their purchase quantity unless selling price changes significantly.
Phosphate: 41 million tonnes of consumption
Phosphate fertilizers, which contain phosphorus (P on the periodic table), are a key nutrient that helps root development and drought resistance. The chemical is important for plant growth because it helps with root growth and seed production.
Potash: 28 million tonnes of consumption
Potassium (K on the periodic table) helps improve crop resistance to lodging, disease, and drought. Potassium isn’t exactly used up by plants, but it’s important for the plant’s ability to withstand extreme cold and hot temperatures, drought, and pests. It also increases water use efficiency and transforms sugars to starch in the grain-filling process. So potassium doesn’t need to be applied every year. This makes potash somewhat more of a price-inelastic product, meaning if prices change a little, farmers may deter purchases. Other factors such as economic outlook and crop prices can have an impact on potash demand.
Fertilizer demand growth story: Food consumption
All of these fertilizers are crucial to maintaining soil fertility. Without adequate soil fertilizer, crop yield can fall, which will negatively affect farmers’ revenues, earnings, and assets. So companies like CF Industries Holdings Inc. (CF), Potash Corp. (POT), Mosaic Co. (MOS), and Agrium Inc. (AGU) play a critical role in the welfare of the global economy. As the world population continues to grow and demand for meat rises, fertilizer demand will only increase over the long term, which is positive for fertilizer producers and the VanEck Vectors Agribusiness ETF (MOO).
