The wireless telecom network and its technologies
The wireless network is also called the cellular network. It makes your mobile and smartphones work over radio signals.
Jan. 16 2015, Updated 2:13 p.m. ET
Wireless network
Wireless telecom came into existence many years after the wireline companies. However, wireless became significant during the last decade. It became particularly important after the beginning of the third generation, or 3G, in 2003. 3G wireless had data capabilities that helped these companies to compete with wireline. However, wireless networks continued to face unique challenges—like managing broadband speeds and network traffic.
Network’s structure
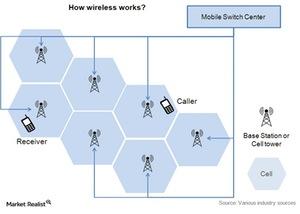
The wireless network is also called the cellular network. It makes your mobile and smartphones work over radio signals. As we can see in the above diagram, the entire wireless coverage area is divided into small cells. Each cell has at least one base station or cell tower. Each cell works at a frequency of radio signals. Mobile phone subscribers can use the network for voice and data services, even if they’re moving between these cells. If a particular cell is congested with traffic, mobile users get the nearest available tower to communicate.
The above diagram is basic. It shows you how a wireless network works. In actual deployments, wireless networks are complex. There are different ways for frequency to be distributed between cells.
LTE
Wireless networks have to be upgraded with new technologies—like LTE (Long-Term Evolution)—to manage the challenge of network traffic, particularly from data usage. Certain devices—like Apple’s (AAPL) iPhone—tend to consume more data.
LTE provides faster internet speeds. It handles higher data usage than previous generations—like 3G. Also, it has low latencies. This means it takes less time for communication and data to travel over the network. It provides an almost seamless customer experience. LTE gives better performance while a customer is on roaming.
Customers prefer companies with the best performing networks. As you can see in the above diagram, in the US, Verizon (VZ) is considered to have the best network performance. It’s followed closely by AT&T (T). T-Mobile (TMUS) and Sprint (S) have the worst network performance.
Please read Why Sprint has seen an improvement in its network performance and Users consume more data on Verizon and Sprint networks to learn more.
