Scientists Build the First Living Robots That Can Reproduce
Xenobots are the first living robots that can reproduce. How can you invest in this innovative technology?
Dec. 1 2021, Published 7:11 a.m. ET

Biotech companies have come to the forefront, especially amid the COVID-19 pandemic. As we become more dependent on biotech, investors are paying attention and following in the footsteps of Amazon founder Jeff Bezos, who has invested heavily in the industry. One fascinating biotech project that's been grabbing headlines is the Xenobot.
Based on frogs and their regenerative properties, Xenobots aren't your typical biotech project. Here's more on this innovative development.
What are Xenobots?
Xenobots are living organisms designed by computers. Their name derives from Xenopus laevis, the Latin name for the African clawed frog. Xenopus means “strange foot” and laevis translates to “smooth.” Xenobots are made from the stem cells of the species. The frog’s stem cells are harvested from embryos and stored in an incubator.
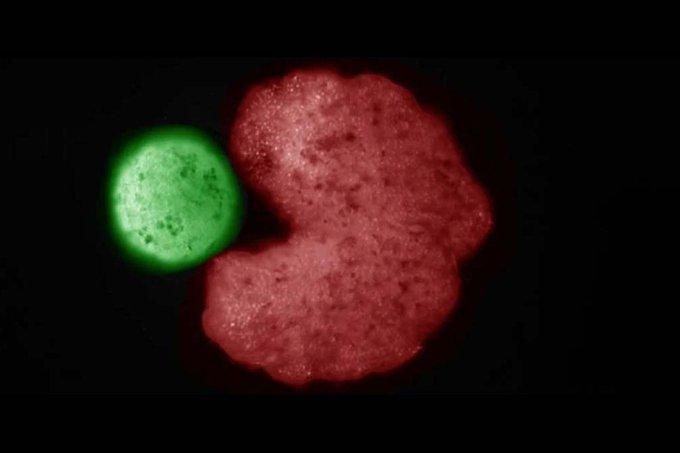
The Xenobots project was started by computer scientists and biologists from Tufts University, the University of Vermont, and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University. The researchers didn’t make the Xenbot project known to the public until early 2020, when they revealed the first version of the Xenobot. It was the first-ever living robot.
Shortly after the original Xenobot project was made public, researchers revealed Xenobots 2.0. The second version had developed legs and was able to travel distances at a much faster rate than the original version. Now, Xenobots 3.0 have been unveiled, making headlines worldwide for the shocking fact that they can reproduce. Although the researchers didn’t report on reproductivity for the previous series of Xenobots, there was some promise—the first ones were able to heal themselves after being cut.
Xenobots 3.0, at only 1 millimeter wide, are incredibly small. The hope is for them to travel in a person’s bloodstream to deliver medicine to needed areas and eliminate toxins and cancer cells.
The use of the African clawed frog for medical research isn’t rare—the amphibian has some of the strongest regenerative properties found in animals today. Scientific reports have stated that the frog’s skin cells play a large role in regeneration after injury. There are other amphibians and aquatic animals with regenerative properties that medtech companies are researching as well.
How to invest in Xenobots
Xenobots are the result of a joint collaboration between researchers at various schools and labs. As there isn’t a specific company behind Xenobots, there are no options available for investing in the revolutionary biotech.
