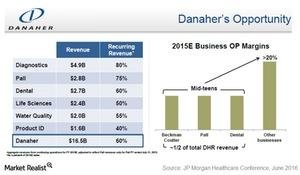
The Key Product Lines That Make Up Danaher’s Diagnostics Business
Danaher’s (DHR) Diagnostics unit, established through the acquisition of Radiometer in 2004, earned $4.9 billion in sales in 2015.
Sept. 2 2016, Published 2:49 p.m. ET
Danaher’s Diagnostics business
Danaher’s (DHR) Diagnostics unit, established through the acquisition of Radiometer in 2004, earned $4.9 billion in sales in 2015. The company expanded this unit by the acquisition of Leica Microsystems in 2005, Vision systems in 2006, Iris and Aperio in 2012, and Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics’ Clinical Biology business in 2015. The Diagnostics segment consists of the clinical laboratory, critical care, and anatomical pathology businesses. Customers are mostly hospitals, pharmaceutical (IHF), and clinical trial laboratories. Although Danaher is a key player in the market, its market position in this business is dwarfed by leaders such as Roche (RHHBY), Siemens, and Abbott (ABT).
Diagnostics: Clinical lab business
Under its clinical laboratory business, Danaher manufactures biomedical (XLV) testing instruments that are used to evaluate samples of body fluids, cells, and other substances. Some of the more common diagnostic systems are used to analyze glucose, cholesterol, urinary tract infections, and kidney and bladder diseases. The company also provides immunoassay and hematology systems used to diagnose more complex diseases. Immunoassay systems provide tests to assess the functioning of the thyroid gland, risks related to cancer and cardiac arrests, and issues related to fertility and reproduction. Hematology tests are used to diagnose blood-related diseases.
Diagnostics: Critical care and anatomical pathology
Under critical care diagnostics, Danaher provides instruments and software used to measure certain critical parameters in the body, such as blood gasses, cardiac markers, anemia, and high-sensitivity glucose. Anatomical pathology products are targeted more towards pathologists, lab managers, and researchers. Products and services within the unit include breast biopsy and tissue-embedding instruments, tools and reagents used to cut thin slices of materials, and software to store and analyze pathology images.
