Nvidia’s Journey from a Startup to the Fastest-Growing Company
Nvidia (NVDA) is currently in a strong position with little competition to its GPU technology. However, it is at risk of entering into a price war with AMD (AMD), which might affect NVDA’s margins.
Aug. 26 2016, Updated 9:04 a.m. ET
Nvidia overview
In this series, we learned about the key factors driving Nvidia’s (NVDA) future growth. This article is dedicated to new investors and gives a snapshot of the company’s business model and the potential risks and opportunities.
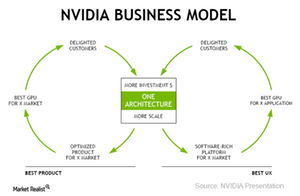
Nvidia was founded in 1993 as a standard PC graphics chip company. Over the past 25 years, it has evolved as a specialized platform company that caters to all segments that use visual computing. In 1999, it invented GPUs (graphics processing units) to enhance the visual computing experience.
GPU
With the slowdown in the PC market and tough competition from Intel (INTC), Nvidia shifted its focus toward its four key markets of gaming, professional visualization, data center, and automotive.
Nvidia uses a platform model, under which it spends most of its capital on developing architecture and then designs chips based on that architecture for four platforms: GeForce platform for gaming, Quadro for professional visualization, Tesla for data center, and DRIVE for automotive.
The company has developed Kepler architecture, Maxwell architecture, and the most recent Pascal architecture.
Tegra
In 2008, Nvidia entered the mobile segment with Tegra processors. However, it exited the mobile space in 2015 due to strong competition from Qualcomm (QCOM). Now, Nvidia is leveraging Tegra processors in the tablet, embedded, and automotive spaces.
Licensing
Nvidia also looked to capitalize its GPU technology by licensing them to others. It entered into several patent lawsuits claiming royalties and managed to strike a five-year licensing deal with Intel, which ends in March 2017.
Potential risks
Nvidia (NVDA) is currently in a strong position with little competition to its GPU technology. However, it is at risk of entering into a price war with AMD (AMD), which might affect NVDA’s margins.
Nvidia is developing technology for autonomous cars but has not yet gained significant success. Many established players are entering this market. There is a risk that any other competitor might develop a successful technology before Nvidia, which would result in the company losing a major market share.
Nvidia still earns a majority of its revenue from gaming, and any slowdown in this sector might impact the company’s revenue. The company has to diversify faster into other segments to mitigate industry-specific risk.
Nvidia depends on third-party foundry TSMC (TSM) for manufacturing. There is a risk that TSMC may prioritize the manufacturing of Apple’s (AAPL) A10 chips over Nvidia’s GPUs. There is also no complete control over the product’s quality, and it faces a risk of poor-quality chips.
