A Porter’s Five Forces Analysis of Kraft Heinz Company
Kraft Heinz faces competition from a huge number of players in the food market, but product differentiation is low between its competitors.
Dec. 31 2015, Updated 8:06 a.m. ET
Porter’s five forces model
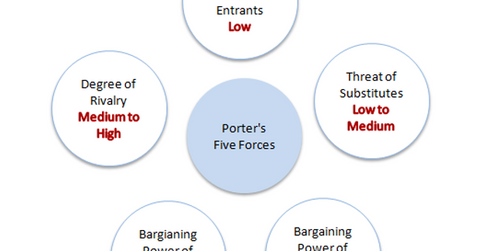
Porter’s Five Forces model is extensively used for assessing the nature of competition and attractiveness of an industry. The model suggests that there are five forces that determine the attractiveness and long-term profitability of an industry or a sector. These include the following:
- the degree of rivalry within the industry
- the threat of substitutes
- the threat of new entrants
- the bargaining power of buyers
- the bargaining power of suppliers
Degree of rivalry within the industry
The food industry size is very large, as the global packaged foods market has reached the size of $2.1 trillion in 2015, according to Statista. The Kraft Heinz Company (KHC) faces competition from a huge number of players in the food market, but product differentiation is low between its competitors. McCormick & Company (MKC), The Hain Celestial Group (HAIN), Mondelēz, and Keurig Green Mountain (GMCR) are some of Kraft Heinz’s main competitors in the industry (XLP).
Threat of substitutes and new entrants
Kraft Heinz has a good, quality brand name in the food market. Low-quality substitutes may not attract customers to switch from Kraft Heinz to other products.
Raw materials required are accessible easily. There are no such government policies that restrict entry in the industry. Therefore, many players can enter the food industry, but they need strong distribution network and strong brand equity to survive in the long run. As the big food companies like to have a wide geographic presence, new players may not compete with them on the geographic front. Exit barriers are also low thus, weaker firms are more likely to leave the market, increasing market share for the remaining firms.
Bargaining power of buyers and suppliers
Kraft Heinz has a large number of customer bases. The company’s products have a good geographic reach with an even distribution between large players and small distributors.
Kraft Heinz has no dependency on any particular supplier, and many of the suppliers depend on Kraft Heinz due to the volume purchase. Raw materials are easily obtained and there are a number of substitute inputs are available.
The Kraft Heinz Company makes up 1.6% of the PowerShares ETF (QQQ). Consumer staples companies make up 7.2% of the holdings of QQQ.
Now let’s take a closer look at the Kraft-Heinz merger.
