Mutual Funds: A Comparative Analysis Using Information Ratios
The information ratio can be used evaluate the performance of an actively managed fund.
Nov. 20 2015, Updated 10:07 a.m. ET
The information ratio
The information ratio can be used to evaluate the performance of an actively managed fund. It can determine how consistently the manager of the fund has generated excess returns for its investors. In simple terms, it is the ratio of the active return generated by the manager over the index return, divided by the active risk taken. The risk taken is measured by the standard deviation of the difference between the returns of the portfolio and the index, which is referred to as the tracking error. The equation is as follows:
Information ratio = (portfolio return – benchmark return)/tracking error
Let’s have a look at the information ratios of our selected funds.
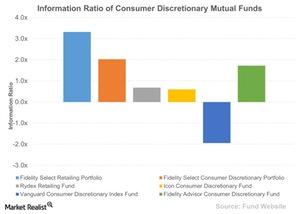
Comparison of the consumer discretionary mutual funds
The Fidelity Select Retailing Portfolio (FSRPX) has the highest information ratio, with 3.3x. This indicates that the managers of the fund consistently achieved higher returns than the benchmark index. In contrast, the Vanguard Consumer Discretionary Index Fund (VCDAX) has a negative information ratio as it has underperformed the index by 0.09% due to investment costs.
