Must know: Geopolitical tensions impact oil prices
A glut in crude oil supply could mean that political tensions in the near term may not impact oil prices.
Nov. 20 2019, Updated 3:47 p.m. ET
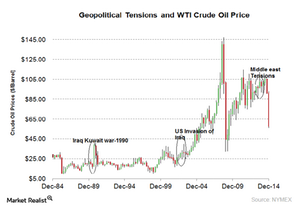
The impact of geopolitical tensions
Geopolitical tensions impact crude oil prices. Political unrest affects production and reduces supply. The consensus of a shortage of oil supply leads to an increase in oil prices. An oil price increase directly impacts the profitability of oil producers such as Chesapeake Energy (CHK), Concho Resources (CXO), BP (BP), Exxon Mobil (XOM) and Marathon Oil Corporation (MRO).
What’s happened in the past?
During the Gulf War that began in 1990, WTI (West Texas Intermediate) and Brent crude oil prices doubled in the beginning of 1990 and dropped ~30% by the end of that year. The United States invaded Iraq in 2003. During this war, Brent crude oil rose by 7% and then declined by 12% by the end of the war.
These geopolitical tensions led to supply disruptions, which increased global crude oil prices. In the Gulf War, supply dropped by ~7%, and in the Iraq War, supply dropped by ~3%. The 2013 Middle East tensions didn’t have much impact on oil prices due to increased production in the United States.
Russia and Ukraine
The recent geopolitical tensions between Russia and Ukraine may slow down the Russian economy. To know more about the Russia-Ukraine crisis, visit the Market Realist series Why the Russia-Ukraine crisis could affect energy investments. Usually, this kind of political unrest disrupts production. Supplies decline, thus impacting crude oil prices. But a glut in crude oil supply could mean that political tensions in the near term may not impact oil prices.
Continue following this series to know more about crude oil demand, the economic crisis, and the implications for oil prices.
