Germany’s Economic Growth and the Role of Rising Inflation
Germany’s expected rise in inflation is concerning as the cost of borrowing has increased across Europe—and this amid all the political uncertainty.
March 13 2017, Updated 9:07 a.m. ET
The impact of rising inflation
Germany’s expected rise in inflation is concerning as the cost of borrowing has increased across Europe—all amid a backdrop of political uncertainty. Yields on the low-rated Eurozone government bonds also rose in January 2017.
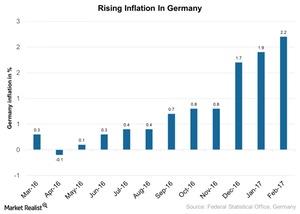
However, German yields (GGOV) fell because it’s considered a safe-haven compared to other bonds. The current increasing trend in inflation poses concerns for European Central Bank authorities. The European Central Bank’s mandate to keep the inflation rate at or around 2% will likely trigger action because the inflation rate in Germany as of the beginning of March 2017 is at 2.2%.
Inflation inches up in 2017
Consumer price inflation jumped in March to 2.2%, as compared to 1.9% in the previous month. Inflation has increased, with the PPI (producer price index) rising to 0.7% in January 2017, exceeding the estimate of 0.3% and hitting a three-month high.
Inflation was meanwhile kept low, mainly due to the fall in crude oil prices and other commodity prices at the beginning of 2016. But as of 2017, consumer price inflation is expected increase considerably, manifesting increased wage costs and increased crude prices.
Import and producer prices
Import and producer prices continued to rise in 2016. According to the Deutsche Bundesbank monthly report as of January 2017, import prices rose 0.3%, and industrial prices rose 1% as of December 2016.
As you can see in the chart above, consumer prices have been sharply rising since December 2016. Overall YoY (year-over-year) inflation rose to 1.7% in 2016, as compared to 0.8% as measured by the national CPI (consumer price index) in 2015. The low inflation in 2015 was mainly due to the decline in energy and commodity prices in 2015.
Impact of rising inflation
German economic data has been recently steady, with its economy expanding and inflation levels moving upward. However, if the inflation rate continues to rise, there will likely be increased pressure to tighten monetary policies, which could be bearish for the stock market (FEZ) (IEV).
Bond markets are also likely to be affected as well, impacting yields. The yield on the ten-year German bond was at 0.25% in January 2017. The sectors that perform better with an increase in inflation are, notably, the ones that are insulated by rising prices.
Companies that can more easily pass rising costs on to consumers are likely to perform better, particularly those involved in commodity stocks. Some of the companies to watch include Metro AG, Tesco (TSCDY), Wm Morrison Supermarkets (MRWSY), and J Sainsbury (JSAIY).
In the next part of this series, we’ll take a closer look at the current unemployment rate in Germany and its impact on economic performance.
