What Are the Key Risks to the Eurozone’s Growth?
The biggest risk to the Eurozone’s (EZU) (IEV) growth is Britain’s exit from the EU (European Union).
June 16 2016, Updated 11:05 a.m. ET
Key takeaways continued.
- Key risks to the outlook include a possible Brexit vote and a renewed refugee influx that poses integration challenges with no discernible economic benefits in the short run.
Market Realist – Brexit and refugee influx are the key risks
The biggest risk to the Eurozone’s (EZU) (IEV) growth is Britain’s exit from the EU (European Union), as it would bring significant economic hardship. The long transition process and heightened uncertainty over Britain’s economic and political relationships with the EU could damage investors’ confidence and may result in less investment. Brexit could severely weaken the already fragile economic recovery in the Eurozone. Additionally, Brexit may affect the Eurozone’s (IEUR) credit rating, leading to higher borrowing costs.
One key element of Brexit is the loss of the world’s premier financial center. Many European businesses access global markets through London. Furthermore, the UK (United Kingdom) (EWU) (EWUS) is one of the strongest proponents of a free market in the EU. It has lent a strong voice to EU’s trade negotiations with other countries. Without the UK, the EU could be less attractive as a trading partner for many countries.
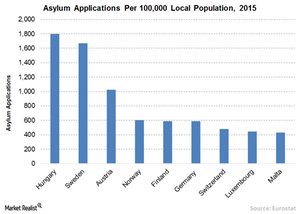
Migrant crisis
The mass influx of migrants from the Middle East is another risk to the Eurozone’s economic outlook. Over the last year, 1.2 million migrants and refugees have relocated to Europe, sparking an economic and social crisis in countries that are already facing economic distress. The huge influx could negatively affect local workers’ wages and jobs. Additionally, to cope with the crisis, countries’ resources are being drained. This has no positive effect on their economies, at least in the short term.
