What’s Qualcomm’s Plan for Its QCT Business?
QCT is Qualcomm’s (QCOM) core business, generating close to 67% of revenues in fiscal 2015. But the capital-intensive nature of the business makes it less profitable.
Dec. 22 2015, Updated 8:05 a.m. ET
Introduction to QCT
In the past articles, we’ve seen that Qualcomm (QCOM) operates in two major segments: QCT (Qualcomm CDMA Technologies) and QTL (Qualcomm Technology Licensing). Now let’s look at the opportunities and challenges that lay ahead for the QCT business.
In its QCT business, Qualcomm designs CDMA (code division multiple access) and 3G/4G (third/fourth generation) mobile chips. The chips are manufactured by third-party foundries such as Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing (TSM).
QCT is the company’s core business, generating close to 67% of revenues in fiscal 2015. However, the capital-intensive nature of the business makes it less profitable, contributing only 26% toward operating income in fiscal 2015.
QCT’s business structure
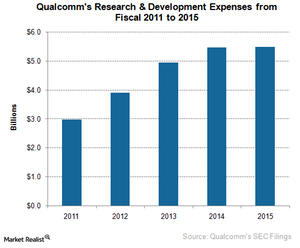
The mobile chip business is highly cyclical in nature and involves a large investment. The success of a new chip depends on how many customers accept the design, creating uncertainty about the chip’s revenue-generating capacity. Each new generation of a chip requires large R&D (research and development) spending. Therefore, most chip makers have high equity and low debt. They conserve cash to support the business during cyclical downturns or the failure of a new chip.
Qualcomm has a debt-to-equity ratio of 0.35. It has a gross margin of 60.0% and a profit margin of 20.8% due to high R&D expenses.
QCT in the industry
On the market front, Qualcomm is losing its monopoly in the mobile chipset market as competition picks up. Samsung (SSNLF) is posing the biggest threat with its entry into the chip designing arena.
Qualcomm plans to overcome the competition by expanding in key adjacent areas such as networking, IoT (Internet of Things), automotive, and data centers. However, the company will face competition even in these areas from Intel (INTC), a leader in the data center space, and NXP Semiconductors (NXPI), a leader in the automotive space.
Another way Qualcomm plans to boost revenue is by introducing innovative products across all three tiers: low, mid, and high. The company is also transitioning to the 14nm (nanometer) node in order to reduce costs and bring operational improvements. We’ll look at these growth strategies in the next part of the series.
The Powershares QQQ ETF (QQQ) has more than 50% of its holdings in large-cap information technology stocks. It has 1.4% exposure in QCOM.
