The Macro Trends that Affect the Global Semiconductor Industry
Consumer trends directly impact the semiconductor industry. For instance, consumers shifted from PC to mobile, negatively impacting Intel’s revenue.
Dec. 31 2015, Updated 7:05 p.m. ET
A quick peek at the global semiconductor trends
So far in this series, we saw that the global semiconductor industry entered a maturity phase, driving consolidation and slow growth. Meanwhile, the Americas, Taiwan, and China are expected to drive growth, and Europe and Japan are expected to recover from negative growth in 2016. If we look at the supply chain, we can see that semiconductor manufacturers are expected to report slow growth while foundries are expected to report strong growth. The outlook for SME (semiconductor manufacturing equipment) providers remains uncertain.
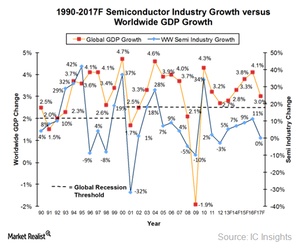
The above trend shows the cyclical nature of the semiconductor industry. Let’s see how macroeconomic factors affect the semiconductor industry.
Correlation between economic cycles and semiconductor sales
As the graph above shows, semiconductor sales are closely linked to the world’s GDP growth. However, there are two exceptions to this trend. The first is the internet bubble in 2001 that led to a sharp fall in the semiconductor industry, and the second is the financial crisis in 2009 that led to negative GDP growth.
A growing economy raises consumers’ spending power. This, in turn, raises the demand for electronics such as mobile, PC (personal computer), and automotive. Thus, consumer electronics companies pump up production to meet the growing demand and place orders for semiconductors, as semiconductors are a key component of electronic products.
Impact of consumer trends
Consumer trends directly impact the semiconductor industry. For instance, consumers shifted from PC to mobile, and this had a negative impact on Intel’s (INTC) revenue as Intel was heavily dependent on PC chips. Japan’s semiconductor industry also missed the mobile trend that led to its fall.
Currently, the trend is moving toward IoT (Internet of Things), and both Intel and Japan (EWJ) are poised to tap the opportunity.
Impact of technology and regulatory trends
The world is shifting away from traditional servers to the cloud. This affected EMC (EMC) and Dell. However, Intel adopted this trend quickly, gaining a share that’s greater than 95% of the data center market.
As the semiconductor manufacturing process is divided across several countries, regulatory issues also affect the profit of the semiconductor companies. For instance, China’s antitrust charges against Qualcomm (QCOM) affected its 2015 revenues. Also, the United States rejected Tsinghua Unigroup’s offer to acquire Micron Technology (MU) due to China’s weak IP (intellectual property) protection.
The outlook for 2016 and 2017 is positive for the overall semiconductor industry.
