Basics About The Capital Gains Tax
The rates for capital gains tax depend on the asset’s holding period. If the holding period is less than one year, short-term capital gains tax is payable.
Sept. 1 2020, Updated 11:59 a.m. ET
The same attitude about taxes persists in the world of investments. Every year, taxable portfolios are assessed to find losses to offset capital gains. But what happens if our resistance to paying taxes leads to suboptimal outcomes? Investors often cite capital gains as a reason to not sell an investment that has done well because doing so would raise their tax obligation. This reluctance to sell is true even if the investment is expensive. Conversely, taking capital losses on investments that have done poorly to offset a gain might mean selling an investment just when it has become cheap.
Market Realist – The following are some of the basics that you need to know about the capital gains tax:
- A capital asset refers to investment in assets like real estate (IYR), precious metals—like gold (GLD) and silver (SLV), stocks (SPY), bonds (TLT) (BND), mutual funds, coins, fine art, and other collectible items.
- Capital gains tax is payable on a capital asset when the original purchase price, in addition to the related expenses, is less than the asset’s selling price.
- The rates for capital gains tax depend on the asset’s holding period. If the holding period is less than one year, short-term capital gains tax is payable. If the holding period is more than one year, long-term capital gains accrue.
- Short-term capital gains are taxed at ordinary income tax rates while long-term capital gains are taxed at 0%, 15%, or 20% depending on the marginal tax bracket that you’re in.
- High income groups are also liable to pay a 3.8% unearned income Medicare contribution tax on their capital gains—in addition to the previously mentioned tax rates. As a result, the highest tax rate applicable is 43.4% for short-term gains and 23.8% for long-term gains.
- Capital losses can be harvested to set off capital gains. As a result, they can bring down the taxpayer’s liability.
- For further details related to filing your taxes, read this IRS note describes capital gains.
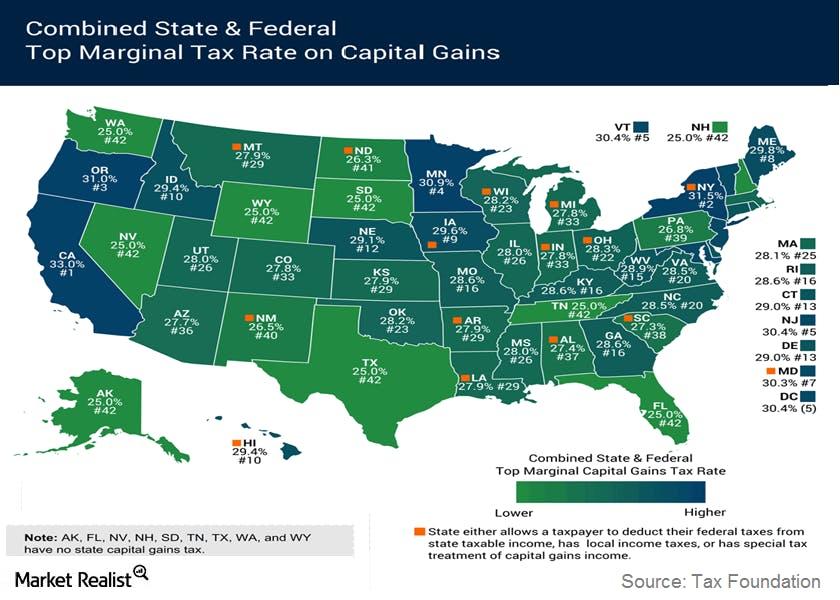
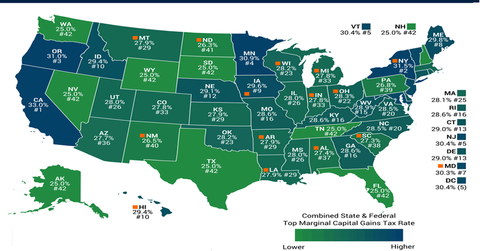
- State and local income taxes, on income from capital gains, are also liable to be paid. The map above shows the combined federal, state, and local top marginal tax rate on long-term capital gains. It shows the tax rate for each state.
- According to estimates by Tax Foundation, the states with the highest top marginal tax rates include California at 33%, New York at 31.5%, Oregon at 31%, and Minnesota at 30.9%. The average long-term tax rate across all states is 28.7%.
In the next part of this series, we’ll discuss how investors’ aversion to capital gains tax impacts their portfolios.
