Data Storage Systems Overview
We live in the “Information Age,” where a huge amount of data is generated every second and storage systems are needed to store this data.
Sept. 22 2015, Published 2:31 p.m. ET
Data storage systems
We live in the “Information Age,” where a huge amount of data is generated every second and technology is needed to store this data. With the advancement in technology, the size of the storage drives keeps shrinking as the capacity keeps increasing.
Internal storage
There are chips located inside the CPU (central processing unit) that store data while an application is in use and then erase it when the application is turned off. Internal memory technologies include DRAM (dynamic random access memory), SRAM (static random access memory), and flash memory chips.
Samsung and SK Hynix together hold a 70% share in the global DRAM market and 50% in the global NAND (negative-AND) flash market. NAND flash is a non-volatile storage technology that can store data even when power is turned off.
External storage
External storage devices store data for a longer period even after the computer is turned off. There are two types of external memory technologies: magnetic disk solid-state drive and optical disk. EMC (EMC) led the external storage systems market with a 31% share in 2014, according to Gartner.
Cloud storage
Cloud storage is an online platform where data is stored and can be accessed from anywhere and at any time. This data is physically stored on servers owned and managed by the hosting company. According to Synergy Research Group, Amazon Web Services (AMZN) led the cloud market with a 28% share in 2014, followed by Microsoft (MSFT) with 10% and IBM (IBM) with 7%.
Enterprise storage architecture
Enterprises deploy storage architecture to store data from multiple computers. There are three types of storage architectures:
- Direct-attached storage devices are directly attached to the server.
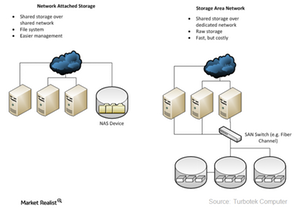
- Storage area networks (or SAN) are high speed networks that connect storage devices to servers. Storage is removed from the server and put in a common place that can be accessed by each networked server using an application.
- Network-attached storage (or NAS) are servers that facilitate file sharing among multiple groups by putting data directly over the network. While the server processes the data, NAS delivers the data to the user.
The PowerShares QQQ Trust, Series 1 ETF (QQQ) has a 4.92% exposure to Amazon and a 7.06% exposure to Microsoft.
