Chainlink 2.0 Staking: Combining On-Chain Code and Off-Chain Resources
Increasing the cryptoeconomic security for DONs (decentralized oracle networks), Chainlink 2.0 has a unique approach to staking.
Aug. 9 2021, Published 3:09 p.m. ET

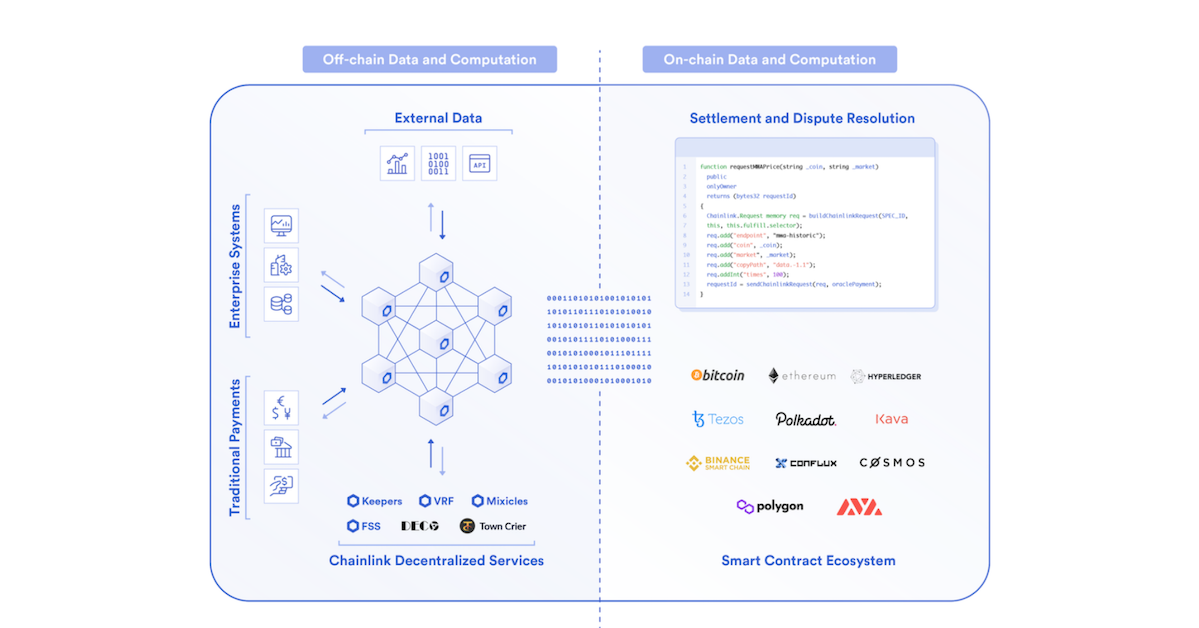
Earlier this year, Chainlink announced Chainlink 2.0, which introduces a new architecture for building hybrid smart contracts where DONs (decentralized oracle networks) offer key capabilities that blockchains can't. Serving as a secure computation layer that partially relies on blockchains for security yet operates with the connectedness and scalability of off-chain systems, DONs are a central component to the unique approach Chainlink takes to staking. Here's what you need to know about staking on Chainlink.
Enabling DONs to perform secure off-chain computations enforces the combining of on-chain code with off-chain resources to build increasingly advanced smart contracts. It becomes a more expansive hybrid infrastructure where developers can further build on. Critical to scaling the security of DONs is creating a robust crypto-economic security model for DONs that maximizes the cost of attack.
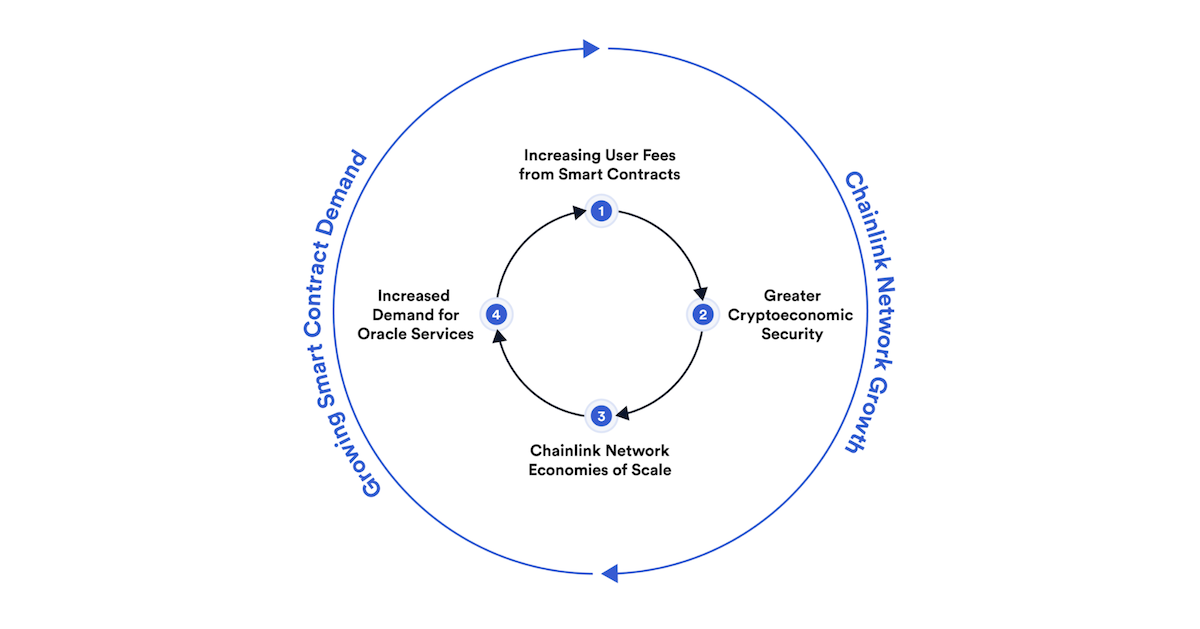
The staking model is unique because it’s designed to protect against an extremely broad class of well-capitalized adversaries.
To achieve a heightened level of tamper resistance, staking is introduced as an advanced system in development where Chainlink nodes lock up native LINK tokens as collateral that can be slashed for malicious and undesirable behavior. Chainlink 2.0 staking aims to achieve a fundamentally different goal than staking within blockchain networks, most PoS (Proof-of-Stake) blockchains use staking mechanisms on a set of transactions ordered into continuously created blocks.
Chainlink 2.0 is focusing more on creating tamper-resistant oracle networks that are reliable and accurately reflect specific real-world events outside of the blockchain. The predominant goal of Chainlink 2.0 staking is to increase the crypto-economic security of DONs, which enables users with greater guarantees around the validity and timeliness of the external data and off-chain computations that their high-value hybrid smart contracts rely on. The Chainlink staking mechanism protects from a broad range of attacks and advanced strategies like bribing nodes with certain nodes on a network

Staking will secure DONs that are tasked with delivering financial market data on the blockchain, a common external data resource required by many DeFi (decentralized finance) applications. Staking consists of multiple components that combine and generate a significant amount of crypto-economic security.
Chainlink 2.0 staking uses service agreements that define how reports should be generated.
Each decentralized oracle network has service agreements that define the number of LINK tokens each oracle node is required to stake. Each network also has other key performance requirements like the extent an individual node’s response can deviate from the aggregated value and how far the aggregated value in an oracle report can deviate from the correct value it should represent.
Any selection of nodes can be chosen to take part in a DON’s service agreement. Nodes can be filtered and selected using existing Chainlink reputation frameworks like the Chainlink Market, which offers a permissionless marketplace that highlights historical node operator performance. A two-tier oracle network design will be used to ensure that the terms of the service agreement are adequately fulfilled. With both low and high-cost tiers, one is used for staking while the other settles disputes of validity generated by the first tier.
Hinging on the "watch dog priority" concept, Chainlink staking adds a twist to how many crypto natives have approached PoS protocols.
