Intel Accelerates 7 nm Road Map to Catch Up with AMD
Intel stock rose 1.3% on May 30 after it unveiled the 10 nm (nanometer) Ice Lake mobile CPU (central processing unit) at Computex 2019.
May 31 2019, Published 2:09 p.m. ET
Intel accelerates road map
Intel (INTC) stock rose 1.3% on May 30 after it unveiled the 10 nm (nanometer) Ice Lake mobile CPU (central processing unit) at Computex 2019. With this, Intel is looking to catch up to its rival Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), which overtook it in the process node technology space by launching its 7 nm PC processors.
Intel’s new management is restructuring the company to help it return to form in the wake of its 10 nm delays. At Intel’s Investor Day 2019, CEO Bob Swan provided a realistic three-year outlook of low-single-digit revenue growth and gross margin contractions for the next three years. The company’s gross margin is expected to contract as it accelerates its process road map to catch up with the competition.
The advanced nodes are capital intensive and require expensive extreme ultraviolet lithography. Intel’s acceleration of its road map will increase its costs and affect its gross margin. Intel plans to launch its 10 nm products in 2019 and 2020 and its 7 nm products in 2021. This looks like an aggressive road map given the issues it’s faced with its 10 nm node. The road map indicates that 10 nm will have a shorter life cycle than 14 nm, further reducing its return on investment given the efforts it put into the node.
Intel’s 7 nm road map
At its Investor Day, Intel stated that its first 7 nm product would be the Xe-based general-purpose GPU (graphics processing unit) for data center AI and high-performance computing, which it will launch in 2021. This GPU will be followed by Intel’s first discrete GPU for PCs and laptops next year.
The Xe product stack will have two different microarchitectures for data center GPUs and client GPUs. The GPUs will incorporate Intel’s advanced Foveros and EMIB (Embedded Multi-Die Interconnect Bridge) package. Foveros is a 3D chip design that stacks together different chipsets, such as a CPU and a GPU.
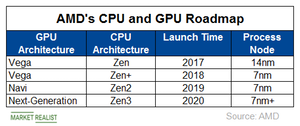
AMD’s CPU and GPU road map currently ends at the 7 nm+ node, which is scheduled for launch in 2020. The company hasn’t provided a road map beyond that point. Intel’s 7 nm processors are expected to be equivalent to AMD’s 5 nm processors, so by launching its 7 nm products by 2021, Intel aims to be back in the process node race.
