NVIDIA Broadens Software Stack to Maximize Data Center Returns
NVIDIA (NVDA) has differentiated itself from other computing accelerator companies like Xilinx (XLNX) and Intel’s (INTC) Altera by transitioning to being an accelerated computing platform company.
Nov. 20 2020, Updated 5:32 p.m. ET
Why is NVIDIA different from other accelerator companies?
NVIDIA (NVDA) has differentiated itself from other computing accelerator companies like Xilinx (XLNX) and Intel’s (INTC) Altera by transitioning to being an accelerated computing platform company. An accelerated computing platform is programmable, compatible with other systems, and has a large installed base and a software stack.
Its rich software stack, which starts with the system architecture, has been driving the adoption of NVIDIA’s GPU (graphics processing unit) accelerated computing platform. To make GPUs easy to use across multiple domains, NVIDIA keeps enhancing and expanding its software stack according to the changing needs of the technology industry.
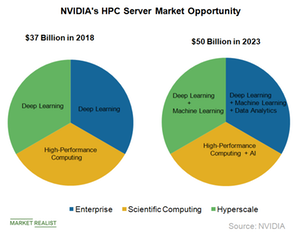
NVIDIA focuses on four data center workloads
At the 2019 Investor Day, NVIDIA’s CEO Jensen Huang stated that the company has developed four architectures for different types of workloads: RTX for graphics, DGX for deep learning and scientific computing, HGX for hyperscale, and AGX for autonomous computers, which are at the edge and disconnected from the cloud.
Jensen Huang stated that data center has many types of workloads and each has a different requirement. In the world of supercomputers, there are two main types of HPC (high-performance computing) machines, a scale-up machine, and a scale-out machine.
Scale-up
Jensen Huang explained that a scale-up machine, as the name suggests, is about the server’s capability to compute one particular thing, which needs 1 billion petaflops (floating point operations per second) of computing performance. Such servers are used in supercomputing and deep learning. NVIDIA’s DGX supercomputers offer that level of performance.
Scale-out
On the other hand, a scale-out machine is a hyperscale datacenter used by Internet companies where hundreds of millions of people may use the website at the same time, and the data center will have to deliver performance in the gigaflops to teraflops range. NVIDIA’s HGX offers scale-out capability.
RTX and AGX are new entrants in NVIDIA data center offerings. NVIDIA is diversifying its data center offerings to maximize returns from one GPU architecture.
Check out all the data we have added to our quote pages. Now you can get a valuation snapshot, earnings and revenue estimates, and historical data as well as dividend info. Take a look!
