NVIDIA Expands its One-Architecture Approach to Automotive
Drive PX Pegasus allows semi-autonomous (and eventually fully autonomous) vehicles to process image information in real time.
Nov. 20 2020, Updated 4:31 p.m. ET
NVIDIA’s one-architecture approach
NVIDIA (NVDA) is working toward offering an end-to-end autonomous driving solution from the data center to AV (autonomous vehicle). Intel (INTC) is also working on an end-to-end solution for autonomous cars.
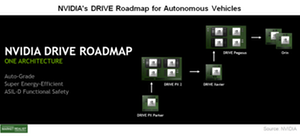
NVIDIA is adopting its one-architecture approach on AV to ease software optimization. At present, an automaker has up to four different computers inside a car to perform four different functions—one to monitor surroundings, one to park the car, one to monitor the driver, and one to drive the car. All these computers might have different operating systems, and each system might have its own software version and maintenance requirements.
NVIDIA looks to address this challenge by bringing all the systems under one architecture with an open platform to optimize all software. Its DRIVE roadmap includes Xavier, Pegasus, and Orin all built on its one-software architecture DRIVE. While this architecture wouldn’t bring any cost savings for automakers in terms of bills of materials, it would significantly reduce their software costs.
Xavier
NVIDIA’s Xavier SoC (system-on-a-chip) processor can collect and process sensor data and understand the outside and inside environment of the car. It has 360-degree surround perception with features such as eye tracking, gesture recognition, and natural language understanding. The SoC notifies the driver of any potential danger outside while monitoring the driver to detect a distracted or drowsy state.
The SoC can also act as a co-pilot, offering adaptive cruise control, lane keeping, and automatic lane changing. All these features are enabled through deep neural networks that can be updated via Wi-Fi or cellular connections. NVIDIA aims to offer its Xavier platform for Level 2 to Level 5 autonomy.
Pegasus
NVIDIA has also unveiled its next-generation automotive AI (artificial intelligence) platform, Pegasus, which the company claims can power completely autonomous vehicles. NVIDIA claims that the Pegasus can deliver more than 320 trillion operations per second, which is ten times faster than its predecessor, Xavier.
Drive PX Pegasus allows semi-autonomous (and eventually fully autonomous) vehicles to process image information in real time. The Pegasus would be made available to automakers in the second half of 2018 and could power Level 5 robotaxis.
ORIN
NVIDIA didn’t give any details about its future platform, ORIN, except that it would feature two chips—one central processing unit and one graphics processing unit.
Next, we’ll look at NVIDIA’s gaming opportunities.
Check out all the data we have added to our quote pages. Now you can get a valuation snapshot, earnings and revenue estimates, and historical data as well as dividend info. Take a look!
