NVIDIA Brings Deep Learning to Robotics
NVIDIA’s robotics strategy is to create a simulation environment, train machines in that environment, and deploy the trained robots in relevant industries.
Nov. 20 2020, Updated 11:49 a.m. ET
NVIDIA in robotics
The two major growth opportunities for NVIDIA (NVDA) in the data center space are training and inferencing. The company is looking to ease the adoption of AI (artificial intelligence) across various industries, and robotics is one vertical that can help it bring AI to the edge.
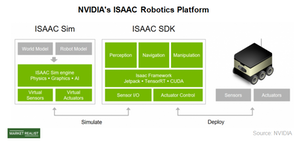
NVIDIA’s Jetson GPU (graphics processing unit) brings AI to edge devices. Supporting its Jetson GPU, NVIDIA has developed the ISAAC robotics platform, which comprises ISAAC SDK (software development kit) and ISAAC Sim.
NVIDIA’s robotics strategy is to create a simulation environment, train machines in that environment, and deploy the trained robots in relevant industries such as manufacturing, construction, inspection logistics, delivery, agriculture, and service. Robots can be used to perform dangerous tasks in oil and gas as well as search and rescue, or critical tasks like elder support.
NVIDIA’s ISAAC
While a robot can be built using the necessary hardware, the biggest challenge in operationalizing robots is training and testing them. At the company’s Investor Day 2018, NVIDIA’s CEO, Jensen Huang, stated that a robot is a complete computer with rich software. Robotics software is more complex than self-driving car software, as there aren’t many rules and the environment is unpredictable.
Creating a complete physical prototype of the real world environment to train a robot is expensive, time-consuming, complex, and impractical. NVIDIA is easing this process through simulation. The ISAAC robot simulator is an AI-based software platform that creates highly realistic virtual environments to train machines and enables data transference to real-world robots powered by Jetson GPUs.
ISAAC Sim
ISAAC includes ISAAC Sim, which enables developers to create extensive test scenarios using deep learning training. Developers can then simulate them in a highly realistic virtual environment using several tools for high-fidelity simulation and advanced real-time rendering.
Once a simulation is complete, developers can transfer the trained system to physical robots to enable them to perceive, navigate, and manipulate using ISSAC SDK. Once the robots are deployed, developers can make changes to the robot testing methodology and trade data between the robot environment and the real-world environment.
ISAAC SDK
ISAAC SDK is an open-source collection of libraries, drivers, APIs (application programming interface), and other tools. The ISAAC SDK framework includes TensorRT inferencing software, CUDA, and Jetpack, which help manage communications and transfer data within the robot architecture to enable robots to perceive, navigate, and manipulate.
At GTC 2018 (GPU Technology Conference), NVIDIA showcased its first reference design, Carter, which is built on the ISAAC platform. Carter is a tiny delivery robot that carts objects around.
Toyota (TM) is using Jetson reference platforms for human support robots: Teal for consumer drones, Enroute Lab for industrial drones, and universities for scale-model autonomous cars.
Next, we’ll look at NVIDIA’s data center opportunity.
Check out all the data we have added to our quote pages. Now you can get a valuation snapshot, earnings and revenue estimates, and historical data as well as dividend info. Take a look!
