Can Intel Keep Its Footing in Technology’s Changing Landscape?
Intel (INTC) has been a dominant name in the technology industry for a long time, holding a strong position in the PC (personal computer) and data center processor markets.
Oct. 30 2017, Updated 11:25 a.m. ET
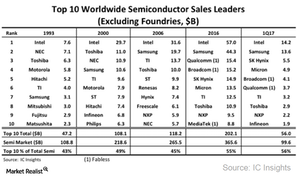
Intel’s competitive advantage
Intel (INTC) has been a dominant name in the technology industry for a very long time, holding a strong position in the PC (personal computer) and data center processor markets. Since 1968, when it was founded, Intel has become a semiconductor giant with several competitive advantages.
Pricing power
Intel has been paying uninterrupted dividends for the past 25 years thanks to its profits and cash flow. Its leading position in the PC and server space and advanced technology allow it to charge a premium price for its processors.
Advanced technology
As we move towards smaller chips, the cost of building leading-edge manufacturing facilities increases. Smaller process nodes improve performance and reduce chips’ costs and power consumption. The high cost of developing and building these nodes creates a major entry barrier and prevents many companies from competing with Intel, which has been enjoying a manufacturing technology advantage over others for a long time. However, Samsung’s (SSNLF) and TSMC’s (TSM) foundries are catching up on manufacturing process nodes.
Brand value
To compete with Intel, competitors must spend huge sums on manufacturing plants and R&D (research and development). Moreover, competitors and new entrants have to compete with Intel’s strong reputation. According to Forbes’s 2017 list of the world’s most valuable brands, Intel is ranked 14th and carries a brand value of $31.4 billion.
Advanced manufacturing technology, economies of scale, and premium pricing have helped Intel create a powerful surrounding ecosystem, with the only competitor being Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). Whereas AMD has struggled for years to compete with Intel in the PC and server space, it now seems to have gained traction with its Ryzen CPU (central processing unit). While Ryzen has helped AMD gain some market share, Intel remains the leader in the PC and server processor markets.
Changing times reduce Intel’s competitiveness
However, the industry is shifting away from PCs towards the IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (artificial intelligence). NVIDIA (NVDA) is at the forefront of this technology. Even Intel is transitioning to the new data-centric world, where the competition is fierce and every company has a shot at market share.
Intel is changing with the technology shift by leveraging its PC and server technology to tap the AI and IoT opportunities. In the last two years, it has made two of its biggest acquisitions, Altera and Mobileye, to grow in the AI and autonomous car markets. In this series, we’ll see if Intel can maintain its dominance in the semiconductor space amid the technology shift.
