What Differentiates AMD’s Threadripper from Competition?
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) has upped the core count of consumer CPUs (central processing unit) from the maximum of ten cores to 16 cores.
Aug. 21 2017, Updated 7:36 a.m. ET
Threadripper is double the mainstream Ryzen
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) has upped the core count of consumer CPUs (central processing unit) from the maximum of ten cores to 16 cores. Unlike Intel (INTC), which disables features of its CPUs to encourage consumers to buy its expensive CPUs, AMD leaves in support for ECC (error-correcting code) memory to help correct single-bit errors.
AMD claims that Threadripper is technically capable of supporting up to two terabytes of RAM (random access memory), but the currently available DIMMs (dual inline memory module) do not support that much capacity.
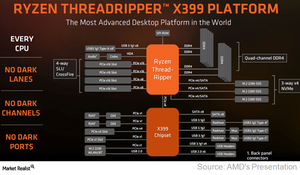
AMD has doubled the specifications of mainstream Ryzen in its Threadripper CPU:
- While the mainstream Ryzen line supports dual-channel DDR4 memory, Threadripper supports quad-channel DDR4.
- While the mainstream Ryzen uses a pin-grid array, Threadripper uses a land-grid array, which is largely used by Intel.
- Mainstream Ryzen chips offer 20 PCIe (peripheral component interconnect express) lanes, whereas all Threadripper CPUs offer 64 PCIe lanes. Of the 64 lanes, four are used to connect to the south bridge and the remaining 60 connect to a maximum of seven PCIe devices such as four GPUs (graphics processing unit) and three NVMe (non-volatile memory). On the other hand, Intel’s $1000, ten-core Core i9-7900X offers only 44 PCIe lanes and its $600 8-core Core i7-7820X offers only 28.
Threadripper is built on the X399 platform and features a new TR4 socket that is incompatible with existing Ryzen chips.
Who should buy Threadripper?
AMD’s chief executive, Lisa Su, stated that Threadripper targets video gamers that play graphics-intensive games and record live video and upload it on YouTube or Twitch. The product is also aimed at videographers that process footage from 4K cameras and drones.
AMD introduced a new gaming mode in Threadripper, as the CPU’s high core count and dual-channel memory controller impact the performance of a game. The gaming mode switches the system to non-uniform memory access, which channelizes all memory access to only one memory controller, thereby lowering latency. The gaming model also tells Microsoft (MSFT) Windows to recognize only eight of the 16 cores in the system, thereby improving gaming performance.
What third party reviewers say about Threadripper
Several third party reviews of AMD’s Threadripper were released on August 10, 2017, and almost all reviews reported that Threadripper beats Intel’s Core in most computing tasks, especially multi-threaded tasks.
Ars Technica stated that Threadripper outperformed Intel’s most powerful customer CPU in most benchmark tests. PC World magazine shared a similar review with reviewer Gordon Mah Ung stating that Threadripper is ideal for “real work” that includes modeling, encoding, and multitasking.
Another review stated that Threadripper helps content creators reduce the time spent on 3D graphics rendering, thereby increasing their efficiency. However, the product doesn’t seem to be of much use to gamers, as it offers little improvement in performance.
Next, we will look at AMD’s Ryzen 3 CPUs.
