Why Intel expects to lead the chip space through its 14nm process
In August 2014, Intel (INTC) shared details about its development with 14nm technology. 14nm succeeds Intel’s 22nm technology.
Nov. 20 2020, Updated 11:28 a.m. ET

Intel’s 14 nm technology
In August 2014, Intel (INTC) shared details about its development with 14nm technology. As the chart below shows, 14nm succeeds Intel’s 22nm technology. 14nm technology uses second-generation Tri-Gate technology for system-on-chips (or SoCs). Tri-Gate technology is Intel’s proprietary 3D transistor technology.

Features that make 14nm superior
When the process shrinks from 22nm to 14nm, size becomes much smaller so that “die-per-wafer” (or DPW) can be increased. With all other things equal, increasing DPW translates to lower cost per die. This results in a less expensive chip after packaging.
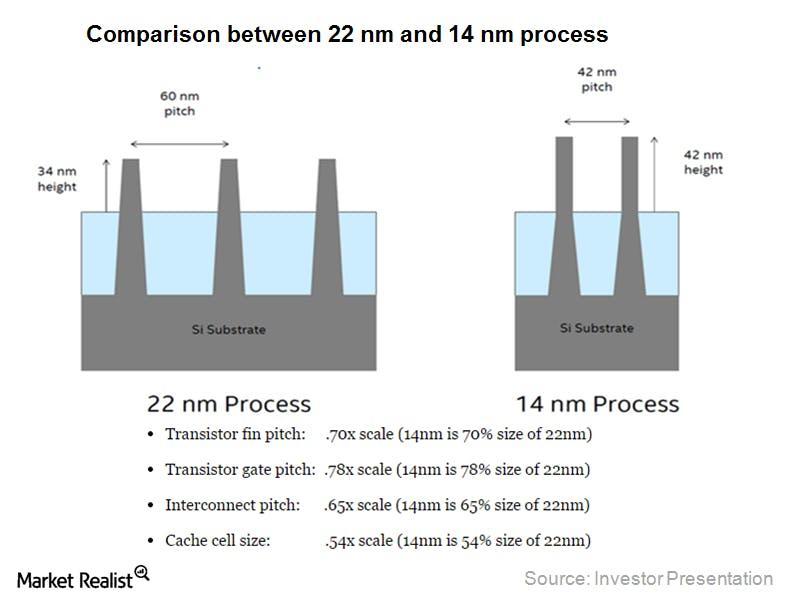
The above chart shows that Intel’s 14nm is impressive on cache cell size and interconnect pitch. Interconnect pitch refers to the minimum space between interconnecting layers.
With transistors, the higher performance usually means less power efficiency. According to Intel, 14nm has a wider dynamic range to scale between phones and server chips when compared to the 22nm process. With 14nm, the leakage, power usage, density, and cost per transistor are reduced.
Performance and performance per watt is increased in 14nm—compared to the previous-generation nodes. Intel boasts that TSMC’s 16nm node yields no area scaling improvement over the 20nm process. TSMC’s 16nm node is expected to be implemented in 2015. TSMC (or TSM) and IBM (or IBM) recently announced their alliance.
Collaboration to enhance adoption of 14nm technology
Owing to its improved features, Intel’s 14nm will be used to build high-performance to low-power products—servers, personal computing devices, and Internet of Things (or IoT). Intel collaborated with Synopsys Inc. (SNPS), ANSYS Inc. (ANSS), Mentor Graphics Corp. (MENT), and Cadence Design Systems Inc. (CDNS) to facilitate the adoption of its 14nm technology by its Custom Foundry customers.
Visit the Market Realist Financial Analysis page to learn more.
