Why Micron’s NAND is an important business segment
These products offer higher performance, reduced power consumption, and better reliability when compared to traditional hard disk drives. This explains the product’s popularity and rapid proliferation as a data storage medium.
May 4 2021, Updated 10:16 a.m. ET
NAND flash memory
NAND flash, with its fast erase and write times, high density and low cost per bit, is ideal for mass storage devices. NAND flash-based storage devices are used in mobile phones, SSDs, tablets, computers, MP3 and 4 players, industrial, automotive, and consumer applications.
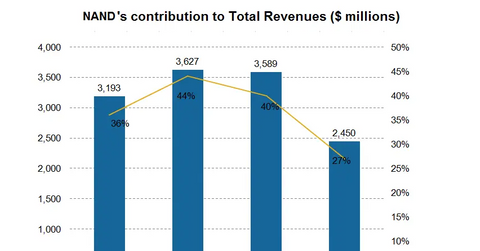
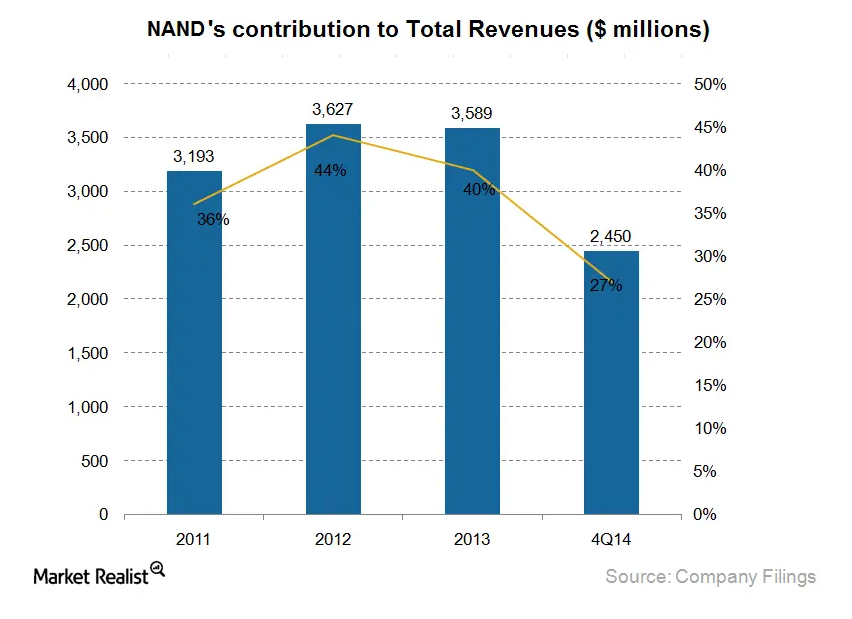
In FY14, this segment contributed ~27% to Micron Technology Inc.’s (MU) overall revenues. NAND is clearly important to the overall growth of the company.
Micron’s solid-state drive, or SSD, business contributes ~45% towards NAND revenues. These products offer higher performance, reduced power consumption, and better reliability when compared to traditional hard disk drives. This explains the product’s popularity and rapid proliferation as a data storage medium.
Owing to low energy consumption and better durability, SSD is the preferred option for embedded systems and mobiles. Exponential growth in mobile computing and slower-than-expected growth in PC shipments have enhanced demand for SSD. This has benefited the NAND segment of Micron’s business enormously.
For more on this topic, read Market Realist’s, Why Microns expects solid-state drives to fuel its business.
Partnerships to enhance position in NAND flash memory space
Micron partnered with Intel Corporation (INTC) to develop NAND flash and other emerging memory offerings. Intel and Hewlett-Packard Company (HPQ) are Micron’s key customers, each contributing ~10% to its revenues.
Micron aims to diversify its NAND business and target attractive end-market applications. Samsung Electronics Ltd. (SSNLF) and Marvell Technology Group Ltd (MRVL) are other leading players in the SSD business.
In a press release, Micron’s management asserted that it expects growth in the segment to be driven by the following:
- chip-level innovation that includes triple level cell and 3D NAND
- investment in system-level capabilities
- additional organizational capabilities
- focused execution on growth and diversifying markets
